- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Week 4- Psychological Disorders
Course: Individual Determinants Of Health (PHE1IDH)
272 Documents
Students shared 272 documents in this course
University: La Trobe University
Was this document helpful?

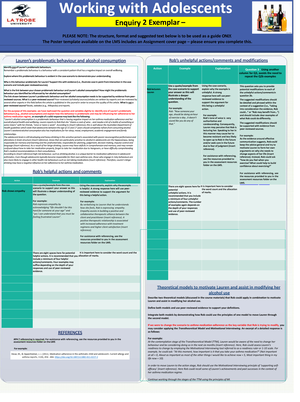
Psychological Disorders
Learning objectives – by the end of this topic, you should be able to:
• Describe the epidemiology of mental health conditions in Australia;
• Identify signs that clients may be experiencing problems with mental health; and
• Apply knowledge of mental health to better understand how people present and interact in
health and human service settings
Health→ State of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
disease or infirmity
Mental health→ A state of wellbeing in which every individual realises his or her own potential, can
cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully and is able to contribute to
her or his community (WHO- Work Health Organisation, 2014)
- Therefore, good mental health means overall state of wellbeing
Mental illness→ Refers to clinically diagnosable disorder(s) which interferes with an individual’s
cognitive, emotion, or social abilities
- Includes wide range of conditions that affects how we feel and think
- Usually first experienced in late teens or early twenties
- Can arise from interaction of genetic vulnerability and stresses in life
- More than 300 mental disorders. Main groups: mood disorders (depression, bipolar
disorder), anxiety disorder (social anxiety disorder), personality disorder
(borderline/narcissistic personality disorder), psychotic disorder (schizophrenia), eating
disorder (anorexia nervosa) and substance abuse disorder.
Anxiety
- When anxious feelings don’t subside. Feeling of worry are ongoing and exist without any
reason or cause.
- Significantly impacts on a person’s ability to cope with daily life
- Normal to feel anxious from time to time (e.g. meeting work deadlines, sitting exams,
speaking in front of a group of people) BUT if a person experiences anxiety, these feelings
cannot be easily controlled.
Main types of anxiety conditions:
- Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD), Specific phobias, Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD),
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), Panic disorder, social phobia
Thoughts
Behavioural
Psychological
Common Symptoms
of Anxiety
-‘I’m going crazy’’
-‘’I can’t control
myself’’
-‘’I’m about to die’’
-People are judging
me’’
-Upsetting dreams of
flashbacks of a
traumatic event
-Find it hard to stop
worrying
-Unwanted or
intrusive thoughts
-Withdraw from or
avoiding fear objects
or situations that
cause anxiety
-Urges to perform
certain rituals to try
and relieve anxiety
-Avoidance (of eye
contact for eg)
-Difficulty making
decisions
Being easily startled
-Increase heart rate
-Shortness of breath
-Vomit, nausea
-Stomach pain
-Muscle tension, pain
-Detached from
physical self
-Sweat, shake
-Dizzy, lightheaded,
faint
-Numb, tingling
-Hot or cold
-Difficult [ ]ing