- Information
- AI Chat
Exam 2017, questions and answers
Psychology
University of Cambridge
Recommended for you
Preview text
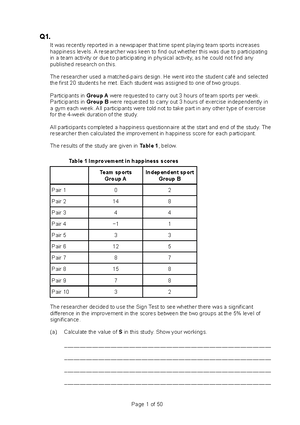
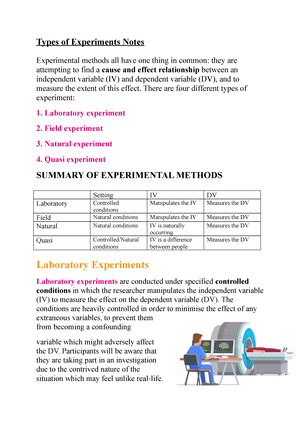
Victorian Certificate of Education Year SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER PSYCHOLOGY Written examination Day Date E L Reading time: *.** to *.** (15 minutes) Writing time: *.** to *.** (2 hours 30 minutes) QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOK P Structure of book Section A B S Number of questions Number of questions to be answered 50 9 50 9 M A Number of marks 50 70 Total 120 • Students are permitted to bring into the examination room: pens, pencils, highlighters, erasers, sharpeners and rulers. • Students are NOT permitted to bring into the examination room: blank sheets of paper and/or correction fluid/tape. • No calculator is allowed in this examination. Materials supplied • Question and answer book of 36 pages • Answer sheet for multiple-choice questions • Additional space is available at the end of the book if you need extra paper to complete an answer. Instructions • Write your student number in the space provided above on this page. • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provided to verify this. • All written responses must be in English. At the end of the examination • Place the answer sheet for multiple-choice questions inside the front cover of this book. Students are NOT permitted to bring mobile phones and/or any other unauthorised electronic devices into the examination room. © VICTORIAN CURRICULUM AND ASSESSMENT AUTHORITY 2017 Version 2 – April 2017 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 2 Version 2 – April 2017 SECTION A – Multiple-choice questions Instructions for Section A Question 1 In an experiment, it is essential to control for extraneous variables so that A. there is a probability that the results will be obtained by chance. B. a valid conclusion can be drawn about the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. C. a valid conclusion can be drawn about the effect of the dependent variable on the independent variable. D. the hypothesis is supported and the results of the experiment can be generalised to the broader population. Question 2 Rylee decided to use the mean as a statistical measure to examine the effect of the consumption of energy drinks on the time taken to complete a jigsaw puzzle. The use of the mean is suitable if the scores are A. clustered around the extreme values. B. clustered around a central score. C. unevenly distributed. D. widely spread. Question 3 Which one of the following sequences best illustrates the consciousness continuum from most aware to least aware? A. induced coma → drowsy → fainted → focused on an examination question B. focused on an examination question → fainted → drowsy → induced coma C. induced coma → fainted → drowsy → focused on an examination question D. focused on an examination question → drowsy → fainted → induced coma SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Answer all questions in pencil on the answer sheet provided for multiple-choice questions. Choose the response that is correct or that best answers the question. A correct answer scores 1; an incorrect answer scores 0. Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers. No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question. PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 4 Version 2 – April 2017 Use the following information to answer Questions 8 and 9. Barry and Terri are at the Australian Football League Grand Final together. They support opposing teams and are both excited and nervous about the game. Question 9 At the end of the game, Barry is experiencing eustress and Terri is experiencing distress. What is the dominant autonomic nervous system division activated during this time for Barry and Terri? Barry Terri A. sympathetic nervous system sympathetic nervous system B. sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic nervous system C. parasympathetic nervous system sympathetic nervous system D. parasympathetic nervous system parasympathetic nervous system Question 10 Parkinson’s disease is characterised by A. decreased dopamine production and improved muscle movements. B. increased dopamine production and improved muscle movements. C. decreased dopamine production and impaired muscle movements. D. increased dopamine production and impaired muscle movements. Question 11 The alarm reaction stage of the General Adaptation Syndrome is usually characterised by an A. immediate release of cortisol into the bloodstream. B. increase in vulnerability to illnesses such as influenza. C. initial increase in blood pressure and body temperature, followed by a decrease in both. D. initial decrease in blood pressure and body temperature, followed by an increase in both. SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Question 8 Both Barry’s and Terri’s excitement and nervousness just prior to the start of the game is likely to produce which of the following physiological changes? A. constricted pupils and muscular relaxation B. constricted airways and bladder relaxation C. dilated pupils and increased release of glucose D. decreased heart rate and increased digestive contractions Version 2 – April 2017 5 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) do not write in this area Question 12 One limitation of the General Adaptation Syndrome as a psychological model of stress with a biological process is that A. a rat’s response to stressors cannot be generalised to a human’s response because the rat’s response is less varied. B. Selye considered the impact of psychological stressors on the human body without considering physiological stressors. C. it does not provide an explanation for why the human body’s level of resistance to stress decreases during the exhaustion stage. D. Selye claimed that, during counter shock, the human body’s level of resistance to stress decreases; however, it is actually known to increase. Use the following information to answer Questions 13 and 14. A psychologist conducted an experiment using the principles of classical conditioning. The experiment investigated the reflexive salivation response in monkeys in response to the presentation of food. After establishing a conditioned response using a bell, the psychologist varied the timing between the sounding of the bell and the presentation of food. Question 13 What were the independent variable (IV) and the dependent variable (DV) in these experiments? IV DV A. presentation of food sounding of a bell B. sounding of a bell presentation of food C. amount of saliva time between sounding of a bell and presentation of food D. time between sounding of a bell and presentation of food amount of saliva Question 14 What were the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) and the conditioned stimulus (CS) in these experiments? UCS CS A. bell food B. food bell C. food saliva D. saliva food SECTION A – continued TURN OVER Version 2 – April 2017 7 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) Question 19 In an investigation into aggression in children, three groups of children were exposed to different conditions: • The first group of children (Group A) observed adults, who were unknown to them, behaving aggressively towards some toys. • The second group of children (Group B) observed adults, who were well-known sports stars, behaving aggressively towards some toys. • The third group of children (Group C) was a control group and this group observed adults playing with some toys in a non-aggressive manner. do not write in this area Each group was then left to play with the toys and was observed for the number of aggressive acts that the children in the group committed. Which one of the following graphs most likely depicts the result of this investigation? A. B. 10 10 mean number of aggressive 5 acts mean number of aggressive 5 acts 0 0 Group A Group B Group C C. Group A Group B Group C D. 10 10 mean number of aggressive 5 acts mean number of aggressive 5 acts 0 Group A Group B Group C 0 Group A Group B Group C SECTION A – continued TURN OVER PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 8 Version 2 – April 2017 Question 20 Shane’s reaction to the image of a snake is called the A. flee-confront response. B. simple phobia response. C. fight-flight-freeze response. D. parasympathetic arousal response. Question 21 Which nervous system is activated during Shane’s reaction to the image of a snake? A. parasympathetic nervous system B. sympathetic nervous system C. central nervous system D. somatic nervous system Question 22 Shane’s thoughts about snakes being likely to attack him and about getting bitten by a venomous snake are examples of A. precipitation. B. memory bias. C. catastrophic thinking. D. an environmental trigger. Question 23 Shane’s psychologist suggests that a group of psychoactive agents known as benzodiazepines may be useful in managing the anxiety associated with Shane’s phobia of snakes. Benzodiazepines imitate the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) by A. activating post-synaptic neurons in the brain to calm the body and reduce arousal. B. activating post-synaptic neurons in the brain to activate the body and increase arousal. C. inhibiting post-synaptic neurons in the brain to calm the body and reduce arousal. D. inhibiting post-synaptic neurons in the brain to activate the body and increase arousal. SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Use the following information to answer Questions 20–23. Shane has an intense and irrational fear of snakes, which has been identified as a phobia. He thinks snakes will attack him and that he will get bitten by a venomous snake. He experiences fear even when he is exposed to a harmless image of a snake in a book or on television. His heart beats faster, he feels sweaty, his mouth feels dry and he leaves the room. To overcome his phobia of snakes, Shane seeks the advice of a clinical psychologist. PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 10 Version 2 – April 2017 Question 29 Garry is driving home from work when his wife calls and asks him to get 10 items from the supermarket. Garry tries to repeat the list over and over to himself, in order, until he gets to the supermarket. Which items is Garry most likely to bring home? A. items 1 and 2, and 8–10 B. the middle four items C. the last five items D. all items Question 30 Kate is learning Spanish as a second language in preparation for a trip she is taking to South America next year. Which of the following identifies where Kate consolidates and stores the new Spanish words in her long-term memory? Where words are consolidated Where words are stored A. hippocampus cerebral cortex B. cerebral cortex hippocampus C. cerebral cortex and hippocampus simultaneously hippocampus D. cerebral cortex and hippocampus simultaneously both cerebral cortex and hippocampus Question 31 Peter, a healthy 56-year-old man, fell off his bicycle while riding to work one day and sustained head trauma. Although he regained consciousness soon after the accident and did not experience any issues with his speech or motor functions, he has been unable to recall any of the events that have occurred since the accident. He can, however, still remember all the memories of his life before the accident and can still recall the events leading up to the accident. A task that Peter should still be able to do is A. recall a new bicycle route to his workplace. B. remember the names of the doctors treating him. C. recite the details of a conversation he had an hour ago. D. use a new piece of equipment after being shown how it works. SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Question 28 Which one of the following statements about short-term memory is most accurate? A. Short-term memory holds only information transferred from sensory memory. B. All incoming information is held in short-term memory for approximately 30 minutes. C. Short-term memory holds all sensory information until it is encoded into long-term memory. D. Short-term memory holds a limited amount of encoded information while it is being processed. Version 2 – April 2017 11 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) do not write in this area Question 32 While rushing out the door to go to school, Sarah accidentally smashed her parents’ antique vase. She was so shaken up by the event that she had trouble sleeping that night and kept replaying the incident in her head for the next two days. The neurohormone involved in the consolidation of Sarah’s memory of the incident is A. GABA. B. dopamine. C. adrenaline. D. a benzodiazepine agent. Question 33 Research by Loftus on the effect of leading questions on eyewitness testimonies has found that A. exposure to leading questions has no impact on an eyewitness’ recollection of events. B. eyewitness memories cannot be manipulated and are, therefore, highly reliable as evidence in court. C. eyewitness memories are reconstructions of events that can be manipulated by information that is given after the event. D. it is unfair to expect eyewitness testimonies to be accurate as people will remember only events that are positive. Question 34 How will the frequency and amplitude of a typical person’s brain waves change between an alert state and a drowsy state? Frequency Amplitude A. increase decrease B. increase increase C. decrease decrease D. decrease increase SECTION A – continued TURN OVER Version 2 – April 2017 13 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) Use the following information to answer Questions 37–40. Kim agrees to participate in a sleep research study conducted by Dr Kapoor. Dr Kapoor uses electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG) and electro-oculography (EOG) to record Kim’s physiological changes over the course of one night while Kim is asleep. do not write in this area Question 37 The type of data Dr Kapoor is generating is best described as A. primary quantitative data. B. secondary qualitative data. C. secondary quantitative data. D. primary repeated-measures data. Question 38 What data about Kim do the EEG, EMG and EOG provide Dr Kapoor with? EEG EMG EOG A. eye position movement patterns brain wave patterns muscle activity B. brain wave patterns muscle activity eye position movement patterns C. brain wave patterns eye position movement patterns muscle activity D. muscle activity brain wave patterns eye position movement patterns Question 39 Dr Kapoor also wishes to investigate the effects of partial sleep deprivation. Which one of the following statements would best describe the findings of the investigation? A. Partial sleep deprivation would have no psychological effect on participants. B. Some participants are likely to suffer severe physical effects for several weeks following partial sleep deprivation. C. After partial sleep deprivation, participants would find it more difficult to perform simple tasks than complex tasks. D. After partial sleep deprivation, participants would find it more difficult to perform complex tasks than simple tasks. Question 40 When Dr Kapoor is studying human sleep patterns, she must A. ensure participant confidentiality. B. debrief participants at the start of the study. C. withhold information from participants about the nature of the study. D. avoid short-term disruption of participants’ sleep patterns for the purpose of the study. SECTION A – continued TURN OVER PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 14 Version 2 – April 2017 Use the following information to answer Questions 41 and 42. The following graphs show the typical sleep cycles for two distinct age groups. Age group 1 awake REM Stage 1 Stage 3 Stage 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 hours of sleep Age group 2 awake REM Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 1 2 3 4 hours of sleep Source: DN Neubauer, ‘Sleep problems in the elderly’, in American Family Physician, May 1999, 59(9), pp. 2551–2558; © 1999 American Academy of Family Physicians SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Stage 2 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) 16 Version 2 – April 2017 Use the following information to answer Questions 45–48. Fraser is under a lot of stress at work and, as a result, is experiencing partial sleep deprivation. He often feels tired during the day and has recently been drinking up to six cups of coffee daily to stay alert at work. Fraser seeks the assistance of a psychologist to deal with his stress, and to improve his overall mental health and wellbeing. Question 46 When Fraser consumes caffeine to increase his level of alertness, an EEG would show a brain wave pattern that has A. low-amplitude and low-frequency waves. B. low-amplitude and high-frequency waves. C. high-amplitude and low-frequency waves. D. high-amplitude and high-frequency waves. Question 47 The psychologist recommends that Fraser try to reduce his daily caffeine intake to two cups of coffee in the morning and to avoid using electronic devices within one hour of going to bed. Fraser believes that this plan is achievable and that he can make these changes over the next two weeks. According to the transtheoretical model of behaviour change, Fraser is most likely in the stage of A. action. B. preparation. C. contemplation. D. pre-contemplation. Question 48 The following week, Fraser restricts his daily caffeine intake to two cups of coffee in the morning. However, he finds it difficult to avoid using his mobile phone within one hour of going to bed as he regularly uses that time to catch up on the daily news by reading it on his mobile phone while in bed. In terms of his two goals of reducing his daily caffeine intake and not using electronic devices within one hour of going to bed, it is most likely that Fraser is in the stages of, respectively A. action and preparation. B. contemplation and action. C. action and contemplation. D. pre-contemplation and relapse. SECTION A – continued do not write in this area Question 45 In terms of the development of mental health disorders, Fraser’s ongoing sleep deprivation could be considered a A. biological predisposing risk factor. B. biological precipitating risk factor. C. psychological precipitating risk factor. D. psychological perpetuating risk factor. Version 2 – April 2017 17 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) do not write in this area Use the following information to answer Questions 49 and 50. Leanne plays the drums in a band with her friends. The band was asked to perform at her cousin’s 21st birthday party. Leanne felt very stressed about performing in front of an audience and, on the evening of the party, she felt sick and asked the band members to perform without her. Leanne stayed at home instead of going to the party. The next time the band performed at a party, Leanne began playing with the band but immediately experienced sweaty palms, an increase in her breathing rate and a rapid pulse as she stood in front of the audience. She stopped playing with the band, said that she felt sick and went home. Leanne has subsequently continued to make excuses and stay at home every time she has been asked to perform with the band at a party because, every time she thinks of playing in public, she experiences feelings of intense fear and worry, shortness of breath, sweating, trembling, nausea and dizziness. Question 49 According to behavioural models, it is likely that Leanne has A. anxiety associated with performing in public that involves precipitation by operant conditioning and perpetuation by classical conditioning. B. stress associated with performing in public that involves precipitation by classical conditioning and perpetuation by operant conditioning. C. enjoyment when performing in public that involves precipitation by operant conditioning and perpetuation by classical conditioning. D. a phobia of performing in public that involves precipitation by classical conditioning and perpetuation by operant conditioning. Question 50 Concerned about her continued reluctance to perform in public, Leanne’s friends suggested that she see a psychologist. The psychologist works with Leanne to develop strategies to minimise her reluctance to perform in public. The psychologist first suggests that Leanne perform with her band in front of a close friend, nominated by Leanne, in familiar surroundings. When Leanne is able to do that without feeling anxious, the psychologist suggests that she practise playing with the band in front of a small group of friends in familiar surroundings. The next step involves Leanne performing with the band in front of a small group of friends in unfamiliar surroundings. Eventually, Leanne was able to perform with the band in public. The treatment used by the psychologist was A. extinction. B. cognitive bias. C. systematic desensitisation. D. cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT). END OF SECTION A TURN OVER Version 2 – April 2017 19 PSYCHOLOGY (SAMPLE) Question 4 (4 marks) Vicky has been having tennis lessons at her local tennis club for a number of years. However, during her last three social matches, where she played with three of her friends at the club, she made a high number of errors when required to swing her racquet backwards. Vicky’s tennis coach suggested that they focus on changing her backwards swing technique over several weeks. a. Describe the role of long-term potentiation and long-term depression, in terms of neural plasticity, when Vicky learns her new backwards swing technique. 2 marks do not write in this area Long-term potentiation Long-term depression b. Once Vicky had mastered her new backwards swing technique, she was selected to play in a competition match at a different tennis club. Prior to the match, the palms of her hands became sweaty and her heart started racing. During the early part of the match, she forgot how to keep the score. Explain how state-dependent cues could have led to Vicky’s inability to remember how to keep the score for the match. 2 marks SECTION B – continued TURN OVER
Exam 2017, questions and answers
Module: Psychology
University: University of Cambridge

- Discover more from:PsychologyUniversity of Cambridge999+ Documents
- More from:PsychologyUniversity of Cambridge999+ Documents