- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Medication Lisinopril
Course: Medical Surgical (NUR425)
418 Documents
Students shared 418 documents in this course
University: Arizona College of Nursing
Was this document helpful?

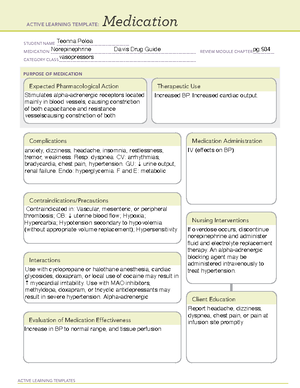
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CLASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
Teonna Poloa
Lisinopril Davis Drug Guide
pg.161
Antihypertensive, Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)I inhibitor
Reduces blood pressure by selectively suppressing
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, inhibits ACE;
prevents conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
Leading to vasodilation, excretion of sodium & water,
retention of potassium by kidney
Give 5 mg within 24 hr of onset
of symptoms, then 5 mg after
24 hr, 10 mg after 48 hr, then
10 mg/day
alcohol (large amounts), probenecide: increased hypotension.
Allopurinol: increased hypersensitivity. Aspirin: decreased lisinopril
effect. Cyclosporine: increased hyperkalemia. Indomenthacin:
decreased antihypertensive effect. Lithium: increased levels of
lithium, toxicity. Avoid high potassium diet: hyperkalemia.
Hypersensitivity, angioedema, and pregnancy (2nd and
3rd trimester. Use cautiously if: pregnant (1st trimester),
breastfeeding, renal disease, hyperkalemia, renal artery
stenosis, CHF, aortic stenosis.
CNS:vertigo, headache, dizziness, stroke, fatigue. CV: hypotension, sinus
tachycardia, chest pain. EENT: blurred vision, nasal congestion GI: nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea, hepatic failure, hepatic necrosis. GU: proteinuria, renal
insufficiency, sexual dysfunction, impotence HEMA: Neutropenia,
agranulocytosis RESP: dry cough, dyspnea SYST: angioedema,
anaphyalaxis, toxic epidermal necrolysis MISC: rash, pruritus, hyperkalemi
Decreased blood pressure in hypertension; decreased
preload, afterload in cardiac heart failure. Used for heart
failure, myocardial infarction, and for clients that are at risk
for a cardiovascular event (to prevent myocardial infarction,
and stroke).
Monitor client's BP, monitor
renal and liver function tests,
monitor renal symptoms, check
potassium levels throughout
treatment.
Decreased blood pressure, edema, moist crackles in
cardiac heart failure (CHF)
Take medication at same time every
day. Avoid high potassium diet. Do not
discontinue abruptly. Only use OTC
cough, cold/allergy medications if
directed by physician to avoid side
effects. Raise slowly from a sitting or
laying position. Teach patient ways to
reduce BP (exercise, stop smoking,
change diet, reduce stress