- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
The Heart (CHP 17) - important key notes for exams
Course: Basic Anatomy & Physiology II (BIO-118-51 )
12 Documents
Students shared 12 documents in this course
University: Camden County College
Was this document helpful?

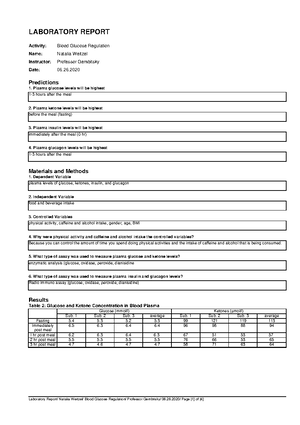
The Heart (CHP 17)
Location & General Features
● Size of a fist
● Weight = 250-300 grams
● Location: in mediastinum; two-thirds lies left of the midsternal line
○ Base of heart = directed toward the right shoulder
○ Apex of heart = points toward the left hip
● Enclosed in the pericardium
● Pericardium structure:
○ Parietal pericardium --> lines the inside of the pericardium
○ Epicardium --> covers the surface of the heart
Layers of the Heart Wall
● Myocardium: mainly cardiac muscle; forms the bulk of the heart
● Endocardium: lines the chambers of the heart
Blood Flow Through the Heart
● Right of side of heart pumps blood into pulmonary circuit
● Left side of heart pumps blood into systematic circuit
● Heart receives no nourishment from the blood passing through the chamber
● Coronary circulation --> blood supply for the heart cells
● Myocardial infarction --> prolonged coronary blockage that leads to cell death
Major Blood Vessels in the Heart
● Aorta
● Superior vena cava
● Inferior vena cava
● Pulmonary artery (which takes oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs where it is
oxygenated)
● Pulmonary veins (which bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart)