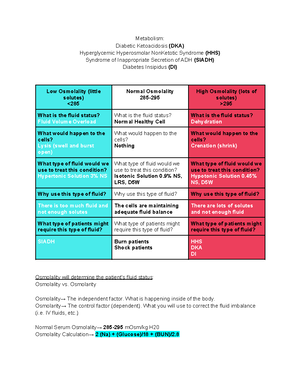
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
RN 231 Hemodynamic case study
Course: Advanced Medical /Surgical Nursing 2 €“ Theory (RN231)
4 Documents
Students shared 4 documents in this course
University: Carrington College
Was this document helpful?

Case Study, Assessment of Cardiovascular Function/Hemodynamic Monitoring
The critical care nurse is mentoring a new nurse on hemodynamic monitoring at the
bedside of a critically ill patient. The patient has a right radial intra-arterial line, and a
right subclavian pulmonary artery pressure monitoring system with a thermodilution
catheter. The critical care nurse demonstrates proper management of the invasive
hemodynamic monitoring lines to the new nurse and obtains the ordered parameters
(mean arterial pressure [MAP], central venous pressure [CVP], pulmonary artery systolic
[PAS], pulmonary artery diastolic [PAD], pulmonary artery wedge pressure [PAWP],
cardiac output [CO], and cardiac index [CI] measurement). The critical care nurse meets
with the new nurse afterward at the nurses’ station and encourages the new nurse to share
what the new nurse understands in regard to invasive hemodynamic monitoring. The new
nurse is currently taking critical care classes on hemodynamic monitoring.
a. What are the indications for the various hemodynamic monitoring methods (intra-
arterial line), CVP line, and the pulmonary artery pressure monitoring system?
What are the differences ?
Arterial Line: Continuous blood pressure monitoring and frequent arterial
blood gas sampling for blood gas analysis, oxygensaturand and acid base
CVP: Monitoring helps determine the fluid volume status for hypovolemia
or fluid overload
Pulmonary Artery Pressure Monitoring System: Estimates cardiac output
for pt with severy hemodynamic instability such as severe heart failure
and shock.
Differences: hemodynamic monitoring depends on the severity of patient.
Arterial lines are used for continuous blood pressure monitoring and
frequent arterial blood gas sampling, while CBP lines provide information
about fluid status and all for fluid and medication administration.
Pulmonary artery pressure monitoring is more invasive and is indicated
for patients with severe hemodynamic instability or complex
cardiovascular conditions that require measurements like cardiac ouput.
b. What are the Normal values for MAP, CVP, PAS, PAD, PAWP, CO, amd CI? DO
NOT COPY AND PASTE: What are the critical values and when would you
perform an ordered intervention (give an example for each) and when would you
contact physician if you don’t have an order?
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAPP: 70-100 mmHg. A MAP below 60 mmHG
is considered critical low and may indicate inadequate perfusion leading
to organ failure. Immidaiate action would be required, such as
vasopressors to increase blood pressure.
Central Venous Pressure (CVP): 2-8 mmHg. A CVP below 2 mmHg is
indication of hypovolemia or inadequate preload. This could lead to
cardiovascular collapse and shock. Fluid resuscitation would be ordered.