- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Human Geography 1
Course: Human Geography (Gt-Ss2) (GEO 106)
28 Documents
Students shared 28 documents in this course
University: Colorado Mountain College
Was this document helpful?

1
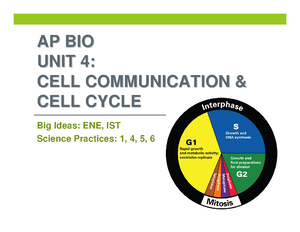
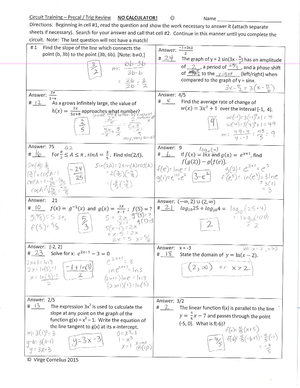
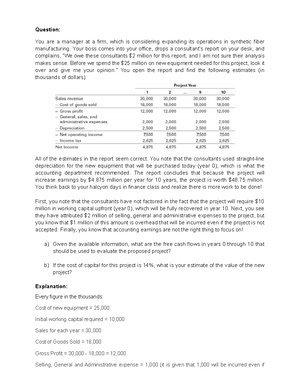
AP Human Geography Outline
Ch. 1 Thinking Geographically
Key Issue 1: How do geographers describe where things are?
Map- a two-dimensional model of Earth’s surface, or a portion of it.
Place- a specific point of Earth distinguished by a particular character.
Region- an area of Earth distinguished by a distinctive combination of cultural and
physical features.
Scale- the relationship between a map’s distances and the actual distances on Earth.
Space- the physical gap between two objects.
Connections- relationships among people and objects across a barrier of space.
Cartography- the science of map-making.
-Earliest surviving maps are from Babylonian clay tablets, (c. 2300 B.C.)
-Aristotle was first to demonstrate that Earth is spherical.
-Eratosthenes was the first person to use the word geography.
Projection- the method of transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a map.
Geographic Information System- (GIS) a computer that can capture, store, query,
analyze, and display geographic date.
Remote Sensing- the acquisition of data about Earth’s surface for a satellite.
Global Positioning System- (GPS) a system that determines one’s exact location on
Earth.
Key Issue 2: Why is each point on Earth unique?
Location- the position that something occupies on Earth’s surface.
Toponym- the name given to a place on Earth.
Place names commonly have:
-British origins in N. America and Australia
-Portuguese origins in Brazil
-Spanish origins elsewhere in Latin America
-Dutch origins in S. Africa
-The Board of Geographical Names was established in the late nineteenth century to be
the final arbiter of names on U.S. maps.
Site- the physical character of a place.
Situation- the location of a place relative to other places.
Meridian- (longitude) an arc drawn between the North and South poles.
Parallel- (latitude) a circle drawn around the globe parallel to equator and
perpendicular to meridians.
Greenwich Mean Time- (GMT) the internationally agreed official time reference for
Earth.
International Date Line- the longitude at which one moves forward or backward 1 day.