- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Human Geogrpahy 2
Course: Human Geography (Gt-Ss2) (GEO 106)
28 Documents
Students shared 28 documents in this course
University: Colorado Mountain College
Was this document helpful?

4
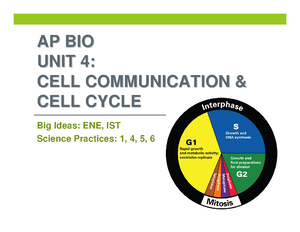
Ch. 2 Population
Key Issue 1: Where is the world’s Population Distributed?
Demography- the scientific study of population characteristics.
Overpopulation- the status of not just the total number of people on Earth, but also the
relationship between the number of people and the availability of resources.
Nearly two-thirds of the world’s population live in 4 main regions:
-East Asia –One-fifth of world pop—Five-sixths live in China alone
-South Asia—One-fifth of world pop—Three-fourths live in India
-Southeast Asia—approx. one-twelfth of world pop
-Europe—One-ninth of world pop
All of the above mentioned population clusters are located w/in 500 miles of ocean coasts
Ecumene- portion of Earth’s surface permanently occupied by humans.
Approximately three-fourths of world population lives on less than 5% of Earth’s
surface. Generally inhospitable lands are:
-Dry Lands too dry for farming cover 20% of land surface.
-Wet Lands too wet for habitation are generally near the equator.
-Cold Lands too frigid to support civilization.
-High Lands too steep, cold, snow-covered for habitation.
Arithmetic density- total number of people divided by total land area.
Physiological density- total number of people divided by total arable land area.
Agricultural density- total number of farmers divided by total arable land area.
Key Issue 2: Where has the world’s population increased?
Crude birth rate- (CBR) total number of live births per every 1000 people per year.
Crude death rate- (CDR) total number of deaths per every 1000 people per year.
Natural increase rate- (NIR) % by which a population grows in a year (excluding
migration).
Doubling time- the number of years needed to double a population (assuming constant
NIR)
Total Fertility Rate- (TFR) the average number of births a woman will have in her
lifetime.
Infant Mortality Rate- (IMR) the annual number of deaths of infants under 1 year old
compared to number of live births.
Life expectancy- the average number of years a newborn can expect to live at current
mortality levels.
Agricultural revolution- domestication of animals.
Industrial revolution- a conjunction of major improvements in technology that
transformed the process of manufactured goods.
Medical revolution- the diffusion of med tech from MDC’s to the LDC’s.
Zero population growth- (ZPG) occurs when TFR = 2.1. (again excluding immigration)