- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Gas Exchange for Ventilation and Perfusion
Course: Human Pathophysiology (NUR 252)
132 Documents
Students shared 132 documents in this course
University: Creighton University
Was this document helpful?

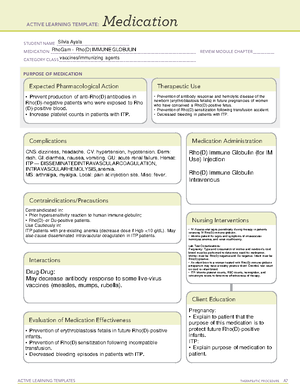
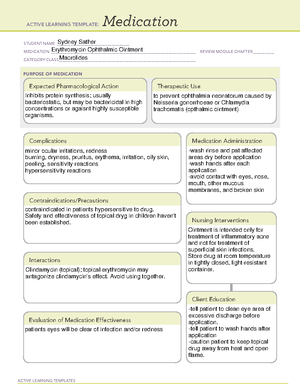
GAS EXCHANGE
1. Ventilation is the movement of oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs.
a. This is impaired if the airway is narrowed or if there is a lack of oxygen available in the
atmosphere
2. Perfusion is the movement of blood into and out of capillary beds of lungs and the body tissues.
a. When perfusion is impaired, oxygen does not reach cells so ischemia may occur
3. Dyspnea is the feeling of breathlessness and increased respiratory effort. This is a subjective
sensation so we must believe them when they say they are short of breath, breathless, or cannot
breathe. If it is more severe, these symptoms might be observed:
a. Nasal flaring
b. Retractions
c. Sweating
d. Tachypnea (increased rate of breathing)
4. Dyspnea on exertion occurs during exercise and goes away when exercise stops.
5. Orthopnea is feeling short of breath when lying flat. Sitting up will relieve this.
6. Dyspnea at rest is an ominous sign.
7. Coughing is a protective reflex that expels secretions and irritants from the lower airways.
a. Acute cough resolves within 2-3 weeks of illness onset
b. Chronic cough lasts longer than 2 weeks; may be due to chronic bronchitis or asthma
8. Changes in the sputum volume, consistency, or color may indicate underlying pulmonary disease.
9. Hemoptysis is expectoration of bloody mucus; the secretions are bright red, frothy, and have
increased pH
a. Usually due to inflammation damaging the bronchi, pneumonia, TB, or cancer
10. Wheezing is high pitched and due to narrowed airways.
11. Rhonchi is low pitched and usually clears with coughing.
12. Crackles are due to fluid in the lungs
13. Pleural friction rub is a grating sound due to inflammation of the pleural space.
14. Hypoventilation is decreased alveolar ventilation caused by airway obstruction, chest wall
restriction, or altered neurologic control of breathing.
a. CO2 is removed slower than it is made which causes hypercapnia
15. Hyperventilation is increased alveolar ventilation that exceeds metabolic demands and is produced
by anxiety, head injury, or severe hypoxemia
a. CO2 is removed faster than it is produced which causes hypocapnia
16. Cyanosis is a bluish discoloration of the skin caused by desaturation of hemoglobin, polycythemia,
or peripheral vasoconstriction.
a. Only apparent when severely hypoxemic so it is not a good indicator of respiratory failure
b. Central cyanosis is due to right to left cardiac shunts and causes blue lips and buccal
membranes
c. Peripheral cyanosis is due to poor circulation, so it is seen in fingers and toes
17. Clubbing of the fingertips is enlargement at the distal portion of the finger and toe; painless and
occurs with chronic hypoxemia associated with diseases that interfere with oxygenation of the
tissues.
18. Chest pain can result from inflamed pleurae, tracheae, bronchi, or respiratory muscles. If it is a
respiratory cause you should be able to push on it and cause the same pain.
19. Hypoxemia is a reduced partial pressure of blood oxygen caused by