- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
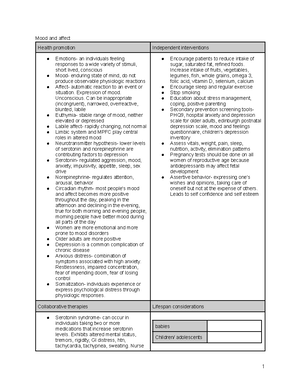
Sensory perception Class Notes
Course: Health Care Concepts II (NSG 211)
45 Documents
Students shared 45 documents in this course
University: Germanna Community College
Was this document helpful?

Sensory perception Class Notes
Trabeculoplasty – trabecular mesh in the corner of the eye allows for drainage
- Can lead to glaucoma
- Clutter free
- Glasses and hearing aids within reach
- Safe and effective care
- Never approach a patient confused with an otoscopy
- Washing hands
Health promotion
- Avoid rubbing your eyes
- Polarized sunglasses are recommended
- **UV light puts us at risk for cataracts – protect your eyes
- Googles for sports – protects from injury, trauma -> causes cataracts
oTrauma causes cataracts
oCan cause closed angle glaucoma
- Cleaning out your ears from earwax
oImpacted earwax
Use warm water (98.6) and a curved syringe to squirt it into the side canal to
flush with 10 mL and then tilt head to get the impacted earwax out
Not cold water, not directly at the ear drum, not when eardrum is perforated,
no Q-tips
Stop if pt becomes nauseated
Psychosocial considerations with eyes/ears
- Isolation is huge
oHearing is more affected bc they don’t admit it and they sit and won’t enter
conversations and stay out of loud, noisy background areas
Someone who talks louder than they should
Person nods consistently
Person doesn’t answer the question you asked
Cupping their ear to hear you better
Lip reading
Asking you to repeat yourself or speak louder
Cataract vs Glaucoma
- Cataracts –yellowing of vision, not just peripheral loss, not just central vision tunneling
- Glaucoma – pain and a halo
Eye drop administration
- Meds in the form of eye drops (glaucoma and cataracts)
- Designed to decrease production of aqueous humor (anterior chamber) coming in OR open the
network to allow for better drainage
- Need to be able to teach how to administer eye drops