- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
NSG124 Exam 3 - Study Materials
Course: Pharmacology (NSG 124)
875 Documents
Students shared 875 documents in this course
University: Herzing University
Was this document helpful?

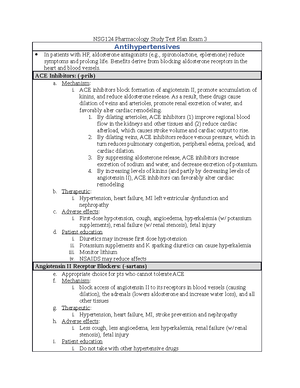
NSG124 Exam 3
Study online at https://quizlet.com/_a295l2
1. I am used in a hypertensive emergency
to lower BP fast.
1) What drug am I?
2) How do I work?
3) What should you watch for?
1) Sodium nitroprusside
2) Vasodilator
3) Hypotension and chest pain
2. Megaloblastic anemia
1) What does megaloblastic mean?
2) What causes it?
3) How do we treat it?
1) Large red blood cells
2) Deficiency of either cobalamin
(vit B12) or folate (vit B9)
3) Pills, vit B12 or folic acid
3. What is the therapeutic lab range for:
1) Lithium
2) Digoxin
1) 0.4-1
2) 0.5-2 or 0.5-0.8
4. Warfarin vs Enoxaparin vs Heparin labs Warfarin = INR
Enoxaparin and Heparin = aPPT
5. I am a mood stabilizer often given
to people with bipolar disorder. I also
used to be an ingredient in 7-Up.
Lithium
6. I will avoid giving IM injections or do-
ing any intervention that could cause
bleeding. I will monitor their aptt/ptt and
be vigilant to S/S of bleeding.
1) What type of med is patient on?
2) Give 2 examples
3) What are S/S of bleeding?
4) What should they avoid at home?
1) Anticoagulant
2) Enoxaparin or Heparin
3) Hypotensive, tachycardia, abd
pain, nausea, cramps
4) Any activity that could cause
bleeding - use soft toothbrush,
careful shaving, need labs, no al-
cohol
7. 1) What is orthostatic hypotension?
2) What common drug types cause it?
3) What will you teach your patient?
1) A sudden drop in BP when you
stand up
2) Any BP med, diuretics, va-
sodilators
3) Stand up slowly, you may feel
dizzy or lightheaded, change posi-
tions slowly
8.
1 / 8