- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Week 13 drug card
Course: Pharmacology (NSG 124)
875 Documents
Students shared 875 documents in this course
University: Herzing University
Was this document helpful?

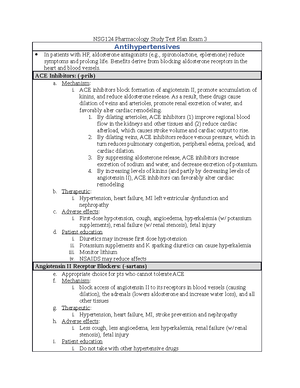
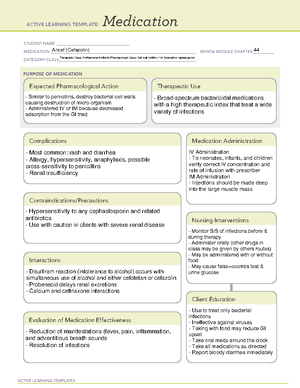
NSG124 Drug Card (must be handwritten)
Uses: Bradycardia <40-50 bpm, brady-dysrhythmia, reversal
of anticholinesterase agents, insecticide poisoning, blocking
cardiac vagal reflexes, decreasing secretions before surgery,
antispasmodic with GU, biliary surgery, bronchodilator, AV heart
block
Nursing Considerations: (labs, VS, etc)
Assess:
• 180 ratios; check for urinary retention, daily output
- VS during treatment, ECG for ectopic ventricular beats, PVC,
tachycardia in cardiac patients
-For bowel sounds, constipation, abdominal distention, if
constipation Occurs add fluids, bulk in diet
-Beers: avoid in older adults; highly anticholinergic, high risk of
delirium, in men decreased urinary flow Evaluate:
Therapeutic response: decreased dysrhythmias, increased
heart rate, secretions; GI, GU spasms; bronchodilation
Side/Adverse Effects:
CNS: Headache, dizziness, involuntary movement, confusion,
flushing, drowsi-
ness
CV: Tachycardia, bradycardia
EENT: Blurred vision, photophobia, dry
eves
Gl: Dry mouth, constipation
Resp: Tachypnea, pulmonary edema
GU: Retention, hesitancy, impotence
INTEG: Flushing, decreased sweating
Route of Administration and Dosage:
Inj 0.05, 0.1, 0.4, 0.8, mg/mL; AtroPen 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 mg/0.7
ML inj prefilled autoinjectors
Adult and child: IM/IV 1-2 mg 920-
30min until muscarinic symptoms disappear; may need 6 mg
every hr
Unlabeled Uses: Stress endocardiopathy
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to belladonna alkaloids, closed-angle
glaucoma, Gl obstructions, myasthenia gravis,
thyrotoxicosis, ulcer alive colitis, prostatic hypertrophy,
tachy-cardia/tachy dysrhythmias, asthma, hemorrhage,
severe hepatic disease, myocardial ischemia, paralytic
ileus.
Precautions: Pregnancy, breastfeeding, children <6 y;
geriatric patients, renal disease, HF; hyperthyroidism,
COPD, hyper-tension, intraabdominal infection, Down
syndrome, spastic paralysis,