- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
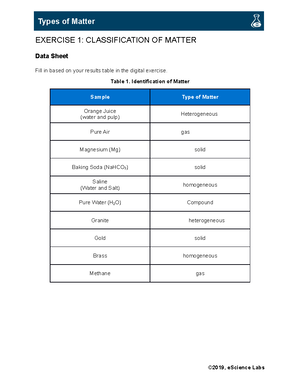
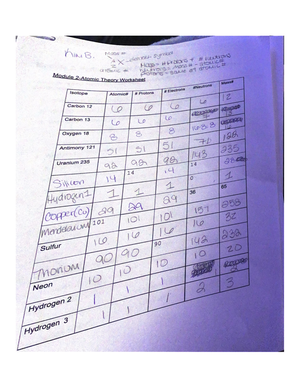
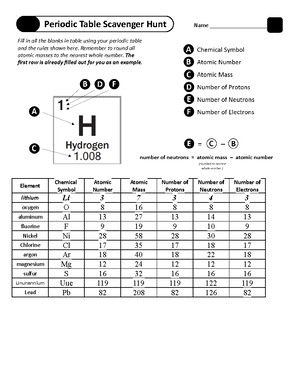
Unit 3 Vocab
Course: Chemistry I (CHEM 111)
16 Documents
Students shared 16 documents in this course
University: Ivy Tech Community College of Indiana
Was this document helpful?

Force strength or power as an attribute of physical action or placement.
Newton equal to the energy that would give a grams of one kilogram an acceleration of one
meter per second
Net Force vector sum of energys acting on a particle or substance
Friction the resistance that one surface or substance encounters when moving over another
Static Friction resists energy that is applied to an substance
Sliding Friction the friction between two bodies that are in sliding contact
Rolling Friction the energy resisting the motion when a body rolls on a surface
Fluid Friction the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other
Air Resistance a energy acting opposite to the relative motion of any substance moving with
respect to a surrounding fluid
Gravity the energy that attracts a body toward the center of the earth
Terminal Velocity constant speed that a freely falling substance eventually reaches when the
resistance of the medium through
Projectile Motion a form of motion experienced by an substance or particle that is projected near
the Earth's surface
Inertia a tendency to do nothing or to will stay the same
Mass a coherent, typically huge body of matter with no definite volume
Weight the energy exerted on the gram of a shape by a gravitational pull
Momentum the quantity of movement of a body, measured as a result of its mass and velocity
Law of Conservation of Momentum the quantity called momentum that characterizes motion
never changes in an isolated group of substances
Electromagnetic Force physical interaction that happens during electrically activated particles
Strong Nuclear Force is the first of the four known fundamental interactions
Weak Nuclear Force is the second out of the four known fundamental interactions