- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Pharm Notes
Course: Nursing Pharmacology
651 Documents
Students shared 651 documents in this course
University: Keiser University
Was this document helpful?

PHARM NOTES
09/22/22
- Histamine role
- Hypersensitivity (I)
- H1 receptor blockers
o1st generation
o2nd generation
Inflammation
Step 1: Transient vasoconstriction (all platelets aggregate into the area)
Step 2: Vasodilation (blood vessels dilate, all chemical mediators (histamine) and cellular
mediators (WBCs) go towards the site
Step 3: Increased vascular permeability
Step 4: WBC full attack
Histamine
- Aids in the secretion of gastric acid, stimulates the parietal cells of the stomach to
produce gastric acid
- VERY important for digestion
- Serves as a neurotransmitter that helps our brain stay awake and active
- Part of the process of inflammation
The problem is that when you have a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction that is IgE
mediated where histamine is released
Do we need histamine? YES
Vasodilation may cause
oBronchospasm/bronchoconstriction
oSneezing
oHives
oSwelling
oCongestion
oDecreased BP
oRisk of anaphylaxis
H1 Receptor Blockers
1st generation
- A drug that is over the counter, Generic: Diphenhydramine, Brand: Benadryl
- They cross the blood-brain barrier, which tells you that they make you sleepy
- Hydroxyzine (must have a prescription for this), Brand: Vistaril
- Chlorphenamine
- Advise the patients to take these at night time
2nd generation
- Claritin (Loratadine), Zyrtec (Cetirizine), Allegra (Fexofenadine), Xysal
(Levocetirizine), Clarinex (Desloratadine)
- They DO NOT or minimally cross the blood-brain barrier, this is why you can take
this in the morning because it does not make you sleepy
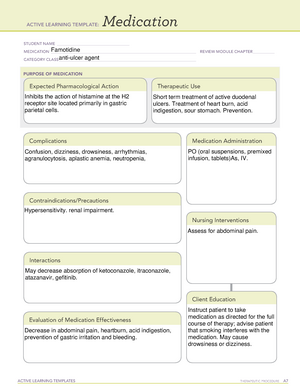
H2 Receptor Blockers