- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
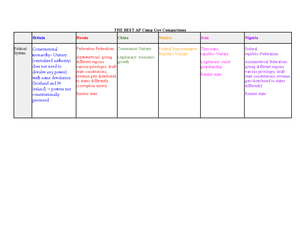
AP Government - Federalism
Subject: AP U.S. Government & Politics
999+ Documents
Students shared 2222 documents in this course
Level:
AP
Was this document helpful?

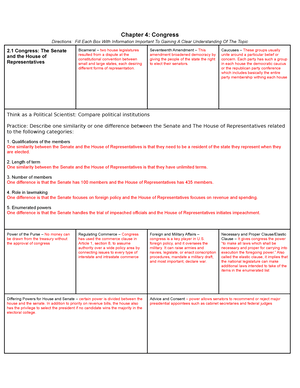
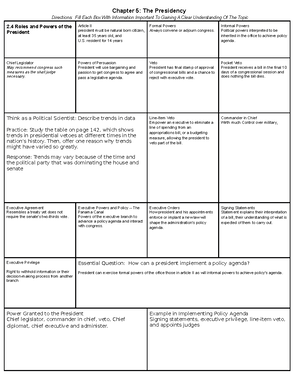
AP Government
Topic: Federalism
Federalism:
●Federalism is the division of power between a central government and regional
governments (states or provinces).
●It allows for shared powers and cooperation between different levels of
government.
Delegated Powers:
●Delegated powers are the powers specifically granted to the federal government
by the Constitution.
●Examples include the power to coin money, declare war, and regulate interstate
commerce.
Reserved Powers:
●Reserved powers are the powers not specifically granted to the federal
government and are reserved for the states.
●Examples include regulating intrastate commerce, conducting elections, and
establishing local governments.
Concurrent Powers:
●Concurrent powers are powers shared by both the federal and state
governments.
●Examples include the power to tax, maintain law and order, and regulate
transportation.
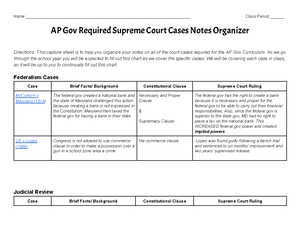
Supremacy Clause:
●The Supremacy Clause in the Constitution establishes that federal laws and the
Constitution itself are the supreme law of the land.
●In case of conflicts between federal and state laws, federal law prevails.
Elastic Clause (Necessary and Proper Clause):
●The Elastic Clause grants Congress the power to make laws that are necessary
and proper for carrying out its enumerated powers.
●It provides flexibility in interpreting and expanding federal powers.
Interstate Relations:
●Interstate relations refer to the relationships and interactions between different
states.
●The Constitution requires states to give full faith and credit to the laws and
judicial decisions of other states.
Intergovernmental Relations:
●Intergovernmental relations involve the interactions and collaborations between
different levels of government (federal, state, local).
●It includes grants-in-aid programs, cooperative federalism, and unfunded
mandates.