- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Cc 1 normal electrophysiology
Course: Critical Care (408)
18 Documents
Students shared 18 documents in this course
University: Loma Linda University
Was this document helpful?

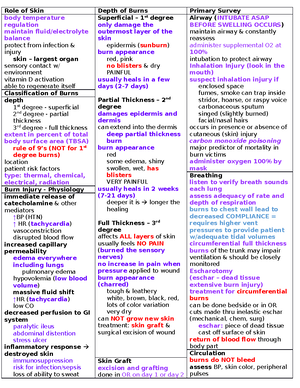
Afterload
ventricular wall tension
during systolic ejection
force to get blood out
systemic vascular resistance
(SVR)
↑ afterload ↑heart
workload
SVR ↑ by factors that
oppose ejection &
anything that affects heart
to pump
Contractility = Inotropy
heart’s contractile force
(how hard heart beats)
Cardiac Index (CI)
CO based on body size
CI = CO/BSA (body surface area)
L/min/m2
Cardiac Output (CO)
volume of blood ejected from
heart in 1min
CO = HR x SV
heart rate (HR) = beats per
minute
stroke volume (SV) = mL of
blood ejected from heart in
one beat
normal CO = 4-8L/min (4-6L/min
at rest)
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
intrinsic/normal pacemaker
60-100 beats per minute
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
secondary pacemaker if SA node
fails AV node kicks in as first
backup
slight pause
40-60 beats per minute
Purkinje Fiber
last chance if SA and AV node
fails purkinje fibers kick in as
second backup
15-40 beats per minute
Automaticity
ability of certain cells to
spontaneously depolarize
(pacemaker potential)
Excitability
given stimulus depolarize
in response
Conductivity
transmit a stimulus from cell
to cell
Rhythmicity
automatic generated at a
regular rate
Contractility
depolarization cardiac
myofibrils shorten in length
Refractoriness
state of cell/tissue during
repolarization
tissue can’t depolarize
regardless of intensity of
stimulus or requires a much
greater stimulus than
normally required
potassium (K+)
intra > extra (more inside cell)
sodium (Na+)
intra < extra (more outside cell)
calcium (Ca2+)
intra < extra (more outside cell)
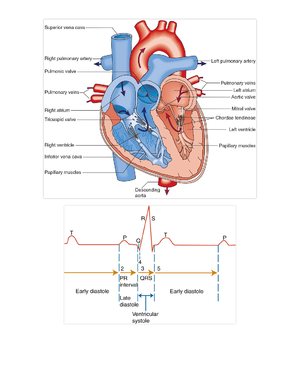
Phases of Action Potential
Phase 0 - Depolarization
fast Na channels open
lots of Na goes in
action potential charge +20 to
+30mV
Phase 1
action potential returns to 0mV
fast Na channels close
Phase 2 - Plateau
slow Na & Ca channels open
K flows out plateau
Ca causes cardiac muscle cell
contraction
Phase 3 - Repolarization
slow Na & Ca channels close
K continues to move out
reestablish resting membrane
potential (RMP)
Phase 4
action potential returns to -80 to
-90mV
Na/K pump work to correct
intra/extracellular ion
concentrations back to
equilibrium
Action Potential
depolarization & repolarization
moves along cell in wave-like fashion
Chemical Gradient
move from high to low concentration
Electrical Gradient
move to area w/ opposite charge
Membrane Permeability
selectivity of membrane to ionic
movement
Intercalated disks
anchor points provides
rapid transmission of
information promote
prolongation of action
potential
Absolute refractory period
cell CANNOT be depolarized
AT ALL
Relative refractory period
cell CANNOT FULLY
repolarize but
could be depolarized if
stimulus strong enough
peak of T wave = vulnerable
to stimuli