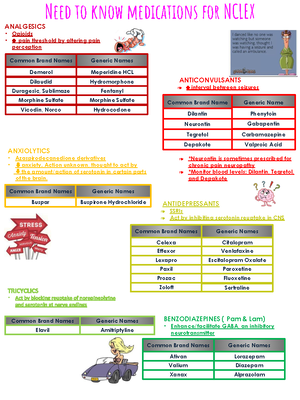
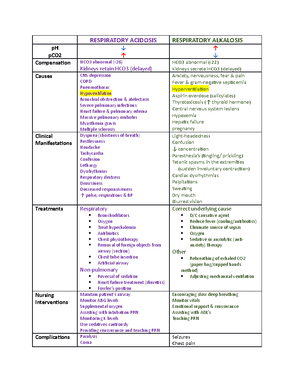
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Cc 11 neuro
Course: Critical Care (408)
18 Documents
Students shared 18 documents in this course
University: Loma Linda University
Was this document helpful?

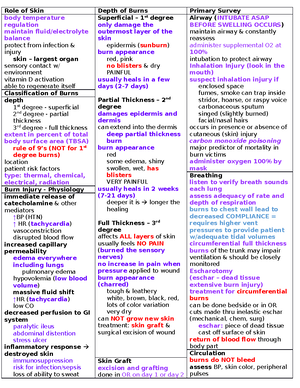
Assessing Neurological
Function
Motor Function*
spontaneous
occurs without external
stimuli & may NOT occur by
request
localization
extremity opposite the
extremity receiving pain
crosses midline of body in
attempt to remove the
noxious stimuli
when you’re trying to illicit a
cough response and the
patient grabs the tube to
relieve them from pain
withdrawal
extremity flexes normally in
response to painful stimuli to
avoid stimulus
decortication
abnormal flexion response
(pull in)
look at shoulder and legs
(core)
may occur spontaneously or
in response to noxious
stimuli
decerebration
abnormal extension
response (come out)
may occur spontaneously or
in response to noxious
stimuli
flaccid
no response to painful
stimuli
Cerebral Hemodynamics
history
clinical manifestations,
associated complaints,
precipitation factors,
progression & family hx
neuro dz
physical exam
LOC
motor function
pupil function
respiratory function
vital signs
complete neuro exam has
NOT been done until all 5
above are performed
analysis of laboratory &
diagnostic data
Na+& BG are notorious for
mimicking neuro problems
intracranial pressure (ICP)
normal: 0-15
>20/10+ min requires
intervention
cerebral perfusion pressure
(CPP)
80-100
kept close to 80 to provide
adequate blood flow to brain
if CPP drops below 80 brain
ischemia may develop
CPP = MAP - ICP
ICP Monitoring Devices
Ventriculostomy
only one w/ CSF access for
drainage/sampling
Subarachnoid bolt or screw
no penetration of brain tissue
less infection rate
Subdural catheter
least invasive, not always
accurate on ICP read
Intraparenchymal catheter
fiberoptic catheter in parenchymal
tissue
hole is punched in dura & catheter
is inserted about 1 cm into brain’s
white matter
Fiber optic transducer-tipped
catheter
can be placed ANYWHERE in
subdural, subarachnoid space, in
ventricle or directly in brain tissue
it is easily damaged and cannot
be recalibrated after placement
Level of Consciousness
goal: alert/oriented x4:
person, place, time, event
alert
responds to external stimuli
confused
disoriented to one of the
following: person, place,
time, event
impaired judgment, safety
awareness, & decision
making
decreased attention span
delirious
disoriented to time, place, &
person
loss of contact w/ reality
often auditory & visual
hallucinations
lethargic
drowsiness
needs stronger stimulus to
awaken
BUT still able to respond
obtunded
less than full alertness
(ALOC)
questions answered w/
minimal response
stupor
responds ONLY vigorous &
continuous stimuli (often
withdrawal)
comatose
no evidence of
responsiveness
absent eye opening or eye
movement to noxious stimuli
Respiratory Patterns*
Cheyne-stokes
rhythmic crescendo &
decrescendo of rate & depth
brief periods of apnea
central neurogenic
very deep, rapid w/ NO
apneic periods
cluster
clusters of irregular gasping
long periods of apnea
ataxic
irregular, random, deep &
shallow
irregular apneic periods
Contributors to Increased ICP*
IV colloids, crystalloids, blood
products
↑ blood flow
vasopressors
↑ pressure ↑ blood flow
Trendelenburg position
↑ blood flow
warming measures
promotes ↑ blood flow
shivering/fever
↑ blood flow
coughing, suctioning, sneezing
agitation, external stimuli
pain
hypoventilation
hypercapnia → ↑ CO2
↑ cerebral blood flow
↑ ICP
↓ seizure threshold
Superficial Reflexes
corneal – cotton ball or eye
drop
blink
cough – suction in ETT if
intubated
gag
plantar