- Information
- AI Chat
Unit 7 - AP Psych notes
AP Psychology (PYSC 1000)
McFatter Technical College
Recommended for you
Students also viewed
- Done How did British and Chinese points of view concerning trade between the two nations differ How were they similar
- Done What is globalization What can a t-shirt reveal about it
- Chapter 05 nursing care of women with complications during pregnancy
- Chapter 09 the family after birth
- Chapter 02 human reproductive anatomy and physiology free
- Chapter 04 prenatal care and adaptations to pregnancy
Related documents
- Chapter 10 nursing care of women with complications after birth
- Chapter 08 nursing care of women with complications during labor and birth
- Chapter 06 nursing care of mother and infant during labor and birth
- AP Psychology Unit 1 - AP Psych notes
- CARE PLAIN FOR POST OP PATIENT FROM SPLEEN RUPTURE
- Presentation Guidelines
Preview text
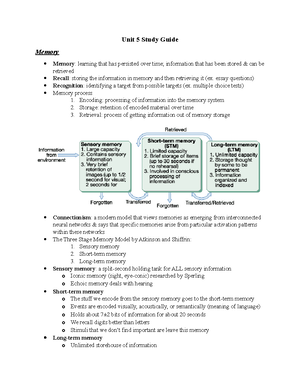
Unit 7 Study Guide
MOTIVATION
General Instinct Theory o Motivation comes from inborn automated behaviors o Problem: instincts only explain why we do small a fraction of our behaviors Drive reduction Theory o Motivation comes from biological needs o Desire to maintain homeostasis o Need ➱ Drive ➱ Drive-reducing behavior Arousal Theory o Motivation to seek optimum level of arousal o Yerkes-Dodson Law: no stress & too much stress = inefficient performance (we don’t want to be overwhelmed nor underwhelmed, we just want to be whelmed) (measures performance & arousal) Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs o Abraham Maslow said we’re motivated by needs & all needs are not equal o Lower level needs need to be satisfied first o
o Highest level is self-transcendence (if it doesn’t say, then self-actualization is it)
Hunger Biological basis of hunger o Hunger doesn’t come from the stomach o It comes from our brain, specifically the hypothalamus Hypothalamus o Lateral hypothalamus Stimulation = makes you hungry Damage to it makes you feel full for the rest of your life o Ventromedial hypothalamus Stimulation = makes you feel full
Damage to it makes you feel hungry for the rest of your life Set-point Theory o Hypothalamus acts like a thermostat o Wants to maintain stable weight o Dieting activates lateral hypothalamus o Gaining weight activates ventromedial hypothalamus Psychological aspects of hunger o Internal = stomach growling o External = something looks or smells appetizing, so you become hungry o The Garcia Effect (taste aversion) Bulimia Nervosa : binging (eating large amounts of food) and purging (getting rid of it) Anorexia Nervosa o Starving themselves to below 85% of their normal weight o See themselves as fat o Many affected people are women Binge-eating disorder o Eating large quantities o Can lead to obesity (being so overweight to the point where it causes health issues) o Mostly eating habits but some people are prone to obesity
Sexual Motivation Kinsey’s studies o Made confidential interviews with 18,000 people in 1950s o Studied sexual behavior in males and females o Made scale of sexuality 0-6, 0 being exclusively heterosexual and 6 being exclusively homosexual (7 is asexual) Masters and Johnson Study o William Masters and Virginia Johnson set out to explore physiology of sex in 1960s o 382 females and 312 males were used in the experiments o They made an institute that was meant to turn gay people straight o Made Sexual Response Cycle Initial excitement Plateau phase Orgasm Resolution with refractory period Psychological factor in sexual motivation: we’re all external when it comes to sex (we see someone and determine if we’re attracted to them) Sexual orientation : an ENDURING sexual attraction toward members of either one’s own gender or of the other gender
EMOTION
Emotion : mix of physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, consciously experienced thoughts, and feelings James-Lange Theory of Emotion o We feel emotion b/c of biological changes caused by stress o The body changes and our minds then recognize the feeling o BODY AND THEN MIND (physiological response, then experienced emotion) Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion o Completely disagree with James-Lange Theory o The physiological change & cognitive awareness must occur AT THE SAME TIME o They believed it was the thalamus that helped it happen o BODY AND MIND AT SAME TIME (physiological response & experienced emotion are separate/it’s not causational) Two-Factor/Schachter-Singer Theory of Emotion o Explained emotions more completely than the other 2 theories o COGNITIVE LABELLING o Biology and cognition interact w/ each other to increase the experience o BODY + COGNITIVE LABEL, THEN MIND (physiological response & conscious interpretation/label, then emotion) Common Sense Theory of Emotion o You think you’re feeling an emotion, so you physically react according to the emotion o MIND AND THEN BODY (emotion & then physiological response) Autonomic nervous system mobilizes body for action & calms it when the crisis passes Sympathetic division of ANS directs adrenal glands to release stress hormones adrenaline & noradrenaline Positive moods & thoughts = LEFT frontal lobe (has rich supply of dopamine receptors) Nucleus accumbens : lights up when people experience natural or drug-induced pleasures Robert Zajonc said we actually have many emotional reactions apart from our interpretations of a situation Polygraphs detect arousal (changes in breathing, cardiovascular activity, and sweat that accompany emotion) Catharsis : emotional release (let it all out) Feel-food, do-good phenomenon : feeling happy makes you help people out Adaptation-level phenomenon : tendency to judge various stimuli relative to those we have previously experienced (ex. getting a raise & getting used to your raise) Relative deprivation : perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself (seeing everyone else getting pay raises & feeling bad about it) Behavioral medicine : integrates behavioral & medical knowledge to apply it to health & disease knowledge Health psychology : provides psychology’s contribution to behavioral medicine
Stress Stress : process by which we perceive & response to certain events (stressors) that we appraise as threatening or challenging Social Readjustment Rating Scale (SRRS) Life Changing Units (LCUs) : marriage, job change, etc. More LCUs = higher SRRS score Higher SRRS scores = more likely to have stress-related diseases Seyle’s General Adaptation Syndrome (response to stressful events) o Alarm o Resistance o Exhaustion (MAKES YOU PRONE TO GETTING SICK) Psychophysiological illness : stress-related physical illness Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) : study of how psychological, neural, & endocrine processes together affect the immune system & resulting health Lymphocytes : the 2 types of white blood cells o B lymphocytes Form in bone marrow Release antibodies to fight bacterial infections o T lymphocytes Form in thymus & other lymphatic tissue Attack cancer cells, viruses, & foreign substances Secretion of stress hormones = less lymphocytes Coping : alleviating stress using emotional, cognitive, or behavioral methods Problem-focused coping : changing stressor or the way we interact with stressor Emotion-focused coping : avoiding or ignoring stressor & attending to emotional needs related to one’s stress reaction Aerobic exercise increases heart & lung fitness; can reduce stress, depression, & anxiety Biofeedback systems allow for people to monitor their subtle physiological responses
o You’re usually unaware that they’re even happening
Different defense mechanisms o Repression : pushing thoughts into our unconscious Explains why we don’t remember our Oedipus & Electra Complexes, according to Freud o Denial : not accepting the ego-threatening truth o Displacement : Redirecting one’s feelings toward another person or object Often displaced on less threatening objects o Projection : believing that the feelings one has toward someone else are actually held by the other person and directed at oneself o Reaction formation : Expressing the opposite of how one truly feels Cooties stage of Freud’s Latent Development o Regression : Returning to an earlier, comforting form of behavior Sleeping with a stuffed animal o Rationalization : Coming up with a beneficial result of an undesirable outcome “I didn’t even want to go out with you anyways, you’re too ugly” o Intellectualization : undertaking an academic, unemotional study of a topic o Sublimation : channeling one’s frustration toward a different goal (sometimes a healthy defense mechanism) Criticisms of Freud: o Only studied wealthy women in Austria o His results aren’t empirically verifiable (aka, you can’t really test them) o No predictive power (you don’t know what defense mechanism someone’s going to use) o Karen Horney said he was a sexist piece of trash because of his “penis envy” concept (a girl feeling jealous of a dude’s pp) o She made up the “womb envy”, meaning that men were jealous of women because of the bond they had with their kids Neo-Freudians’ Psychodynamic Theories o Erik Erikson’s 8 stages of psychosocial development o Carl Jung and his concept of the “personal” and “collective” unconscious o Collective unconscious : reservoir of images derived from species’ universal experiences & is believed to explain why people in different cultures are share myths & images (like mother = symbol of nurturance) o Alfred Adler & his ideas of superiority and inferiority o Adler also talked about birth order & how it played a part in personality (if you’re the youngest, middle, oldest, or only child) Psychoanalysis today o Couch sitting in movies (“Interesting, and how did that make you feel?”) o Transference is likely to happen
o Main goal is to get into your unconscious, pull out manifest content (storyline), and talk about latent content (meaning behind manifest content)
Getting into the unconscious o Hypnosis o Dream interpretation o Free association : having them randomly talk to themselves & then interpreting conversation o Projective tests delve into the unconscious (TAT and Inkblot) Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) o Giving subject a picture that is ambiguous (can have several meanings) & ask them what’s happening o Their answers reveal the manifest content & they can then discover the latent content Rorschach Inkblot Test o The most widely used projective test o A set of 10 inkblots designed to identify people’s feelings when they’re asked to interpret what they see in the inkblots Terror-management theory : theory of death-related anxiety; explores people’s emotional & behavioral responses to reminders of their impending death
Trait Theories of Personality They believe that we can describe people’s personalities by specifying their main traits Traits like laziness and ambition are thought to be stable over the course of our lives Nomothetic (Big 5) Theory o The same traits can be used to describe all personalities o McCrae and Costa o Introversion-Extroversion Scale o The five traits that all personalities have: OCEAN Openness to experience (creative, curious, & willing to try new things) Conscientiousness (hardworking, responsible, & organized) Extraversion (outgoing & sociable) Agreeableness (easy to get along with) Neuroticism (consistency of mood) o Factor analysis is used to see clusters & scores on these tests Idiographic theorists : o Using same set of traits to classify everyone is impossible o Each person may have a few traits that are unique to them (selfish may be important to describe one person but not another) o Gordon Allport Cardinal traits : most dominant Central traits : general characteristics that shape & influence behavior Secondary traits : traits only seen occasionally o Hans Eysenck Found that behavior could be represented by 2 dimensions
External locus of control = something outside of you controls your fate (God or something) External locus of control leads to learned helplessness (giving up & not changing because you think that you can’t help make your situation better) Self-serving bias : readiness to perceive ourselves favorably
Assessing Personality Most common way to assess personality = self-report inventories MMPI = Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory Test must be reliable (same results if repeated) & valid (measures what it says to measure)
Unit 7 - AP Psych notes
Course: AP Psychology (PYSC 1000)
University: McFatter Technical College

- Discover more from:
Recommended for you
Students also viewed
- Done How did British and Chinese points of view concerning trade between the two nations differ How were they similar
- Done What is globalization What can a t-shirt reveal about it
- Chapter 05 nursing care of women with complications during pregnancy
- Chapter 09 the family after birth
- Chapter 02 human reproductive anatomy and physiology free
- Chapter 04 prenatal care and adaptations to pregnancy
Related documents
- Chapter 10 nursing care of women with complications after birth
- Chapter 08 nursing care of women with complications during labor and birth
- Chapter 06 nursing care of mother and infant during labor and birth
- AP Psychology Unit 1 - AP Psych notes
- CARE PLAIN FOR POST OP PATIENT FROM SPLEEN RUPTURE
- Presentation Guidelines