- Information
- AI Chat
Divalproex sodium - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
Pharmacology Review (NURSE 252)
Olympic College
Recommended for you
Students also viewed
- Valproate sodium - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Valproic Acid - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Depakote - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Carbatrol - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Depakene - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Lamictal - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
Preview text
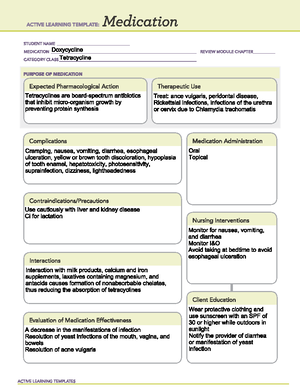
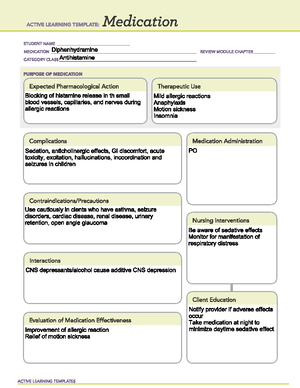
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Me dication STUDENT NAME mepication Divalproex sodium REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER category cLass Mood stabilizer and antiepileptic PURPOSE OF MEDICATION Expected Pharmacological Action Increase levels of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS Therapeutic Use Suppression of seizure activity. Decreased manic episodes. Decreased frequency of migraine headaches Complications alopecia, rashes, visual disturbances, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, constipation, appetite, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, weight gain, tremor, ataxia, agitation, dizziness, headache, insomnia, sedation, confusion, depression May increase levels of carbamazepine, diazepam, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rufinamide, topiramate, or zidovudine dosage adjustments of these medications may be necessary increase levels of decrease dose of propofol use with topiramate may increase risk of hypothermia and hyperammonemia with or without encephalopathy, imipenem, or meropenem may decrease valproate levels may decrease valproate separate administration 3 hr Interactions Increased risk of bleeding with warfarin levels and toxicity may be increased aspirin, carbamazepine, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, erythromycin, or felbamate CNS depression with other CNS depressants, including alcohol, antihistamines, antidepressants, opioid analgesics, MAO inhibitors, and inhibitors and other antidepressants may decrease seizure threshold and decrease effectiveness of valproate, meropenem, phenobarbital, phenytoin, contraceptives, or rifampin may decrease valproate levels Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness Decreased seizure activity incidence of manic episodes in patients with bipolar disorders frequency of migraine headaches ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Medication Administration PO IV Rectal Nursing Interventions Assess location, duration, and characteristics of seizure activity. Institute seizure precautions mood, ideation, and behavior frequently Prophylaxis: Monitor frequency and intensity of migraine headaches: Assess geriatric patients for excessive somnolence for suicidal tendencies, especially during early therapy. Restrict amount of drug available to patient. Risk may be increased in children, adolescents, and adults 24 yr Client Education Instruct patient to take medication as directed. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until effects of medication are known. Tell patient not to resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and consult health care professional before taking any new medications, especially CNS depressants. Caution patient to avoid alc
Divalproex sodium - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
Course: Pharmacology Review (NURSE 252)
University: Olympic College

Recommended for you
Students also viewed
- Valproate sodium - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Valproic Acid - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Depakote - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Carbatrol - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Depakene - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses
- Lamictal - Mood stabilizers with antiepileptic uses