- Information
- AI Chat
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Was this document helpful?
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
CSCI 340 Notes
Course: Operating Systems Principles (CSCI 340)
16 Documents
Students shared 16 documents in this course
University: Queens College CUNY
Was this document helpful?
This is a preview
Do you want full access? Go Premium and unlock all 11 pages
Access to all documents
Get Unlimited Downloads
Improve your grades
Already Premium?

CSCI 340 Operating System
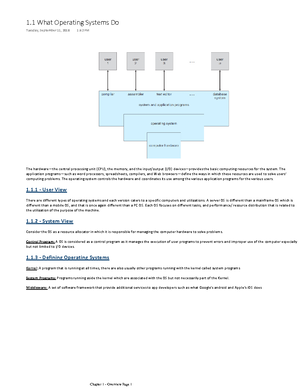
Definition: An Operating System (OS) is a program that manages the computer
hardware. It also provides a basis for Application programs and acts as an
intermediary between computer Users and computer Hardware. Examples of
Operating systems are Windows, Linux, Ubuntu, MacOS X, iOS, Android.
Types of OS:
-Batch OS: Batch operating system is an operating system in which the system
performs multiple jobs of similar types of functions. This group of multiple jobs
with similar tasks is also called a batch. Each batch consists of jobs of the same
type like a batch of C++ files, java files, etc. Every job is the collection of
programs, input data, and control instruction. One after another batches gest
processed inside the CPU. O.S was very simple and its task was to process jobs
one after another. Examples of Batch OS are the Payroll system, Bank
Statements, etc.
-Time-Sharing OS: A time-sharing operating system is an operating system
that allows many users to share computer resources. In other words, time
sharing refers to the allocation of computer resources in time slots to several
programs simultaneously. Also known as Multitasking Operating system. The
task can be from a single user or different users. The time that each task gets to
execute is also called quantum. After the time interval is over OS switches over
to the next task. Example: Multics or Unix.
- Distributed OS: In distributed operating system multiple autonomous
interconnected computers communicate with each other using a shared
communication network. Independent systems possess their own memory and
CPU. These are referred to as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems.
These systems’ processors differ in size and function. The major benefit of
working with these types of operating systems is that it is always possible that
one user can access the files or software which are not actually present on his
system but some other system that is connected within this network. I.e. remote
access is enabled within the devices connected to that network. Example
LOCUS etc.
Why is this page out of focus?
This is a Premium document. Become Premium to read the whole document.
Why is this page out of focus?
This is a Premium document. Become Premium to read the whole document.
Why is this page out of focus?
This is a Premium document. Become Premium to read the whole document.