- Information
- AI Chat
Ch 20 Mammalia
Zoology (BIOL 212)
Saginaw Valley State University
Preview text
Amniota [tetrapods with an amnion] Follow the other brick road ... 1 Synapsida Early tetrapod lineages [1 pr temp. fen.] Diapsida [2 pr temp. fen.] anthracosaurs temnospondyls Amphibia [extant & extinct lineages] Lissamphibia [extant only] 1 2 Mammals have a synapsid ancestry from pelycosaurs through the diverse therapsids and ... pelycosaur Carboniferous [300 mya] to Permian extinction [280 mya] therapsids
- mammalian skeleton
- largely homodont
- enlargement of temporal fenestrae
- intermediate middle ear ear ossicles Disappeared in the Late Triassic [200 mya] 2 &otaller only, one brightly colored communication
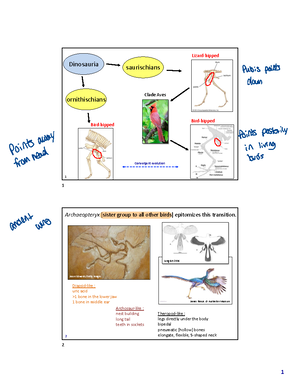
3 into the cynodonts, which survived the Permian extinction. The cynodonts yield the Clade Mammalia. Morganucodon Probainognathus synapsids mammals cynodonts pelycosaurs therapsids 3 What are mammalian traits?
- hairy, 2. homeothermic, 3. endothermic, 4 vibrissae quills Underfur: 1 type of hair 4 smaller in Size Crabbit size Clas ~ Insulation 1 -underfur
- defensive I mechanorecepters
- touch
Mammals have other 5. unique features associated with the integumentary system. 7 antler horn Pronghorn: branched horn Antler Horn Branching [yes / no] Composed of? Growth/shed pattern Who has it and by sex. 7 8 Mammals are 6. heterodonts, 7. diphyodonts, 8. thecodonts with 9. precise occlusion. occlusion different shape : different functions a. Incisors ----- b. Canines. ----- c. Premolars. ----- d. Molars. ----- Ruta. From Klembara et al. 2014 heterodont vs. homodont 10. Secondary palate 8 derived born inside from -> catin han Sheeth ↓ horn Rams A dif shape -a set In sockes ~ < upperd Lower together
9 Diet diversity is reflected in teeth, skulls, & digestive systems Fermentation in ruminates; mutualism with ciliophorans and/or bacteria. Longer intestines in herbivores, sometimes with coprophagy. 9 10 Mammals have a 11. muscular diaphragm, 12. neocortex, 13. vascular placenta in most, 14. turbinate bones, and 15. well-developed olfaction. Turbinate bones hold epithelial tissue, filter air using cilia and warm incoming air. Negative-pressure ventilation with a diaphragm and loss of lumbar ribs. 10 Shorter the track carnivores more plants
- longer digestive tract
- doesn't extract all nutrients Ruminents = division of stomach Capandex Cagnative ~ abilities sure O -preslation venO have f lung insure S 7 dominal
- assist in O Cavity ↑of bore spiral fis of pressure rentia because small increases that on the way Smell out in f
#bones in ↓ones in middle 2 ower Jaw ear includes D: apsids 7 5 dentory & Columella Stapes & centory ability
aveus-ircus
are
entire
msmal ( stapes ·
soit
easi
Lower - Centary - Squamosal (15) LSKUK) Indicates drum ear Outer ear inner d sapes mallus ↓ ↓ stirrup hammer
- Cochlea
- llens-Incus- stapes ear - Ma pinna- drum enstation tube Canals ->balance semicircular
13 This transition is documented in the fossil record. phase 3: mammal: switch to only a dentary – squamosal jaw joint phase 1: Diapsid, early synapsid: quadrate – articular jaw joint Probainognathus phase 2: some cynodonts: 2 jaw joints 13 14 ~5500 extant species diversified rapidly from a shrew-like, endothermic, nocturnal ancestor as dinosaurs disappeared. Mammalia Prototheria Theria Metatheria Eutheria Earliest mammals in late Triassic had developed nearly all mammalian traits. 14 articulate quaduatearesittingmoved ↓ ear aroundmiddle as dentral gets bigger saw becomes not as strong = many pieces 2, bonein 4 bones middle ear 2 sets of Jaw Joints
17 Metatherians are marsupials. Embryos are nourished by a vascularized yolk sac-chorion placenta [choriovitelline]. Altricial young: jellybean size Remains for several months Reproductive investment is via prolonged lactation and offspring at multiple stages of development. Marsupium: pouch for joey Embryo hatches from a shell membrane after several days in the uterus. animals.sandiegozoo/animals/marsupial animals.sandiegozoo/animals/marsupial In pouch for up to a year 17 18 Metatherians diversified on islands, where they filled ecological niches analogous to those of placental mammals. Harry Burrell Thylacine [wolf]. Extinct in 1936. Easyscienceforkids Bandicoot [rabbit]. Sugar glider [flying squirrel]. wombat [groundhog]. true-wildlife.blogspot/2011/04/wombat.html Scitechdaily Australiananimallearningzone washingtonpost Marsupial mouse [mouse]. Joe McDonald. Visuals Unlimited thinglink Marsupial mole [mole]. Tasmanian devil [wolverine/bobcat]. Kangaroo [cavy] 18 live birth mother growth when posts ⑧ · All tine lactation Yolk Sac invested he prolonged period after year on Fort -naMr to No
abtesvoin
in
19 The only marsupial in MI is the opossum. Originating in SAm, they dispersed north after the rise of the Panamanian isthmus. ”playing opossum” : thanatosis the other white meat? evolutionforskeptics.files.wordpress/2016/12/marsupial-distribution.jpg?w= Marsupial spp distribution Great American Interchange: ~3 – 2 ma 19 20 Placental mammals [eutherians] invest in longer gestation times, a chorioallantoic placenta, and precocious young. Integrated and deeply embedded fetal membranes [villi] in the uterine wall. placentanetwork instagram .com /p/BUv7hrwD16I/?taken-by=kindred_birth Umbilical cord contains stem cells. Precocial caribou calf 20
roading
to
re - playing clearin it 5 ~ anymore - can talke live birth parti Chloron + Alantion care of gesturation - ambia at themselves long period villi or Humano
####### intrees
Al X ~ up peruse G
seeit
Ch 20 Mammalia
Course: Zoology (BIOL 212)
University: Saginaw Valley State University