- Information
- AI Chat
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Was this document helpful?
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Anatomy and physiology semester 1 final review
Course: Human Anatomy And Physiology I (PSIO 201)
179 Documents
Students shared 179 documents in this course
University: The University of Arizona
Was this document helpful?
This is a preview
Do you want full access? Go Premium and unlock all 3 pages
Access to all documents
Get Unlimited Downloads
Improve your grades
Already Premium?

Anatomy and Physiology Semester 1 Final Review
Chapter 1: Be able to define the directional terms and the common anatomical planes of the body. As well as the various body cavities.
1. The clavicle is superior to the sternum.
2. The hip is superior to the ankle.
3. The ears are lateral to the nose.
4. The umbilicus is anterior to the lumbar vertebrae.
5. The skin is superficial to the femur.
6. The study of the function of the human body is known as physiology
7. The heart is anterior to the vertebral column.
8. The plane that divides the body into equal left and right sides: Sagittal Plane
9. The plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions: Coronal Plane
10. The plane that divides the body or organ into superior and inferior portions: Transverse Plane
11. The thoracic vertebrae are superior to the lumbar vertebrae.
12. The abdominopelvic region that contains most of the stomach: Epigastric
13. The urinary bladder would be found in which region? Hypogastric Region
14. Review the body cavities and know what organs you’d find in them.
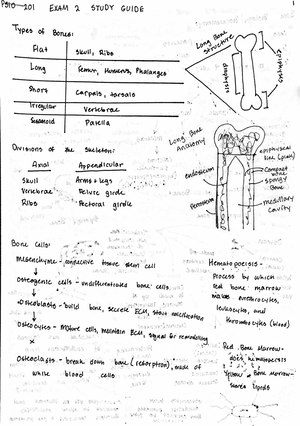
Chapter 4: Be able to classify and recognize the four major tissue types of the human body, including their physiology.
15. Organ: a part of an organism that is typically self-contained and has a specific vital function, such as the heart or liver in humans
16. System: an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform complex functions for
the body
17. Histology: the study of tissues and cells under a microscope
18. List the levels of structural organization (simplest to most complex): Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
19. What type of tissue would you find a lot of fat in? Adipose Tissue
20. List the four major types of tissue. Connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue
21. What specific type of tissue would store red marrow? Connective tissue
22 What are the major functions of cartilage? The ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support on
bony areas where there is a need for flexibility
23. Which type of muscle tissue is involuntary and striated? Cardiac muscle
24. Which type of muscle tissue is involuntary and nonstriated? Smooth muscle
25. What is a significant function of simple cuboidal epithelium? Where would you find it? Absorbing or secreting material into the
Why is this page out of focus?
This is a Premium document. Become Premium to read the whole document.