- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Brain Structures and Functions Reading
Course: Human Anatomy And Physiology I (PSIO 201)
179 Documents
Students shared 179 documents in this course
University: The University of Arizona
Was this document helpful?

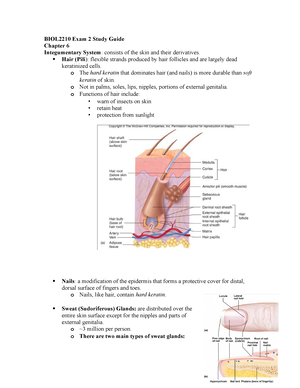
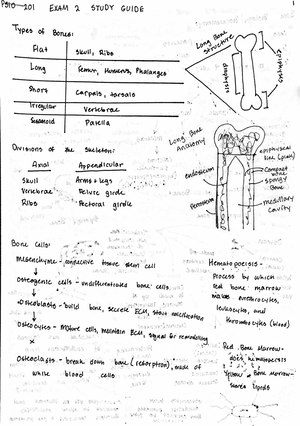
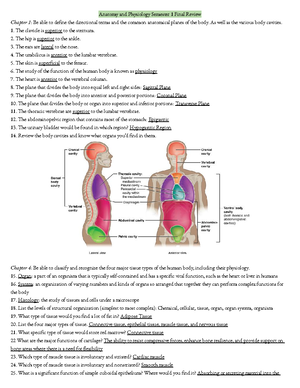
Brain
Structures
&
Functions
rd
.
14
.
Ib
:
Grey
&
white
Matter
grey
matter
-
stat
of
nevrosomas
+
dendrites
+
synapses
=
cortex
over
arebellum
&
cerebrum&
nuclei
surrounded
by
while
matter
white
matter
deep
to
the
cortical
grey
matter
in
most
of
the
brain
-opposite
in
the
spinal
cord
white
matter
composed
of
tracts
14
.
39
:
The
Medulla
oblongata
embryonic
hindbrain
-
myerencephalon
&
metencephalon
myelencephalon
becomes
I
adult
structure
-
medulla
oblongata
-most
caudal
part
of
the
brainstem
-immediately
superior
to
foramen
magnum
all
newe
fibers
connecting
brain
=o
spinal
cord
pass
through
medulla
ascending
fibers
:
sensory
1st
:
Irid
,
3rd-order
fibers)
descending
fibers
:
motor
14
.
3b
:
The
POUS
menterphalon
-
pous
&
arebellum
-2
.
S
Cm
Long
pons-
handles
unconscious
processes
(sleep-wake
,
breathing
(
cranial
newes
v-VIII
begin
lend
in
the
pous
-Auctions
:
*
sensor
loves
(hearing
,
equilibrium
,
touch)
*
facial
sensations
*
Motor
roles
leye
movement
,
facial
expressions
,
chewing
swallow
,
urination
,
etc
.
)
-
reticular
formation
in
the
pous
contains
nuclei
for
sleep
,
respiration
,
&
posture
14
.
31
:
The
midbrain
mesencephalon
-
midbrain
midbrain
:
short
legment
of
the
brainstan
,
connecting
the
hindbrain
forebrain
14
.
3d
:
The
Reticular
Formation
the
RF
is
a
loose
web
of
grey
matter
...
rus
vertically
through
all
levels
of
the
brainstem
&
upper
spinal
cord
key
functions
:
*
somatic
motor
control
*
sleep
&
consciousness
*
cardiovascular
control
*
habituation
#
pain
modulation
-