- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
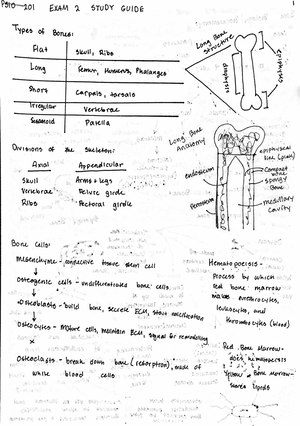
Crystallization Worksheet
Course: Human Anatomy And Physiology I (PSIO 201)
179 Documents
Students shared 179 documents in this course
University: The University of Arizona
Was this document helpful?

Crystallization Worksheet
1) List some common examples of crystals found in nature.
Some examples include rock salt, table salt, diamonds and gemstones, snowflakes,
proteins, sugar (such as rock candy), malaria parasites and insulin.
2) What drives crystal growth?
The main driving force is supersaturation which occurs when more solute exists than the
solvent can dissolve.
3) Draw the surface of a crystal face. Where would a drug molecule bind to inhibit crystal
growth?
I hope a picture works as well.
A drug molecule would bind to the kink sites to block further crystal growth.
4) What are the four types of kidney stones?
Calcium oxalate, struvite, uric acid, cystine
5) What must be considered when designing new drugs?
Efficacy: full inhibition of crystal growth
Potency: small amount of drug causes full inhibition
Cost: feasibility to manufacture