- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
System Disorder Diabetes Mellitus UTI
Course: High Acuity (Nurs4528)
40 Documents
Students shared 40 documents in this course
Was this document helpful?

ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
System Disorder
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS __________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
ASSESSMENT SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE
Alterations in
Health (Diagnosis) Pathophysiology Related
to Client Problem Health Promotion and
Disease Prevention
Risk Factors Expected Findings
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures
Complications
Therapeutic Procedures Interprofessional Care
Nursing Care Client EducationMedications
Diabetes Mellitus
Blood glucose alterations
Monitor: vitals, BG levels, I&O
& weight, skin integrity and
healing status of wounds,
sensory alterations, dietary
practice, exercise patterns.
Self-monitored blood glucose: is essential
to management of diabetes.
Measurements should be checked at a
minimum before meals and at bedtime.
8-hr fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL
or greater. *Random blood glucose of 200
mg/dL or greater. *Oral glucose tolerance test
of 200 mg/dL or greater. *Glycosylated
hemoglobin (HbA1C)
Partial or complete metabolic deficiency of
insulin by destruction of pancreatic beta
cells for Type 1, Type 2 arises when the
body fails to use insulin properly.
Hypoglycemia: <60mg/dL
Hyperglycemia: >250mg/dL
Routinely checking of BG levels.
Exercise regimen, Diet pattern.
Genetics can predispose a person to type 1 or
2. *Toxins and viruses can predispose an
individual to diabetes leading to type 1.
*Obesity, physical inactivity, triglycerides
greater than 250 mg/dL, and hypertension can
lead to insulin resistance
Assess Allergies
Safety precaution
when
administering
meds.
*Refer the child and
family to a diabetes nurse
educator for
comprehensive education
in diabetes management.
*Check the accuracy of the strips with
the control solution provided. *Keep a
record of the SMBG that includes time,
date, serum glucose levels, insulin
does, food intake, and other events
that can alter glucose levels
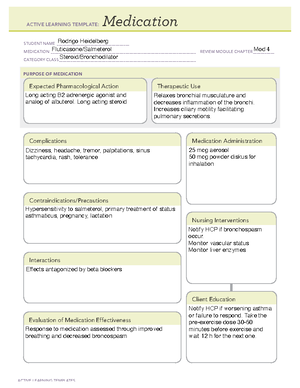
*Insulin *Insulin
pumps *Insulin
injections
*Assist with exercise
plan. *Discuss child
illness management
guidelines
DKA (Diabetic
Ketoacidosis): An
acute,
life-threatening
condition
characterized by
hyperglycemia
(glucose
>330mg/dL),
ketonemia,
glycosuria,
ketonuria, and
acidosis (pH 7.30
and bicarb 15
mmol/L)