- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Concept Map Fluid Shifting
Course: Intro to Nursing (N3290)
33 Documents
Students shared 33 documents in this course
University: The University of Texas Medical Branch
Was this document helpful?

1
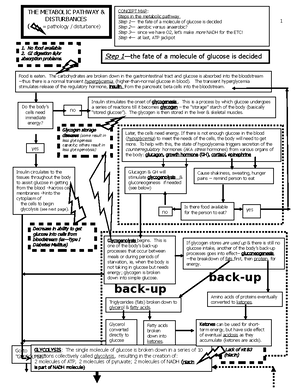
Concept map 1: Steps in determining which way fluid shifts
1. For our studies about fluid shifts, Na+ (& NaCl) & proteins will be the solutes involved. They are the main solutes that drive
fluid shifts, which are based on
osmosis
--movement of
water
from area of lower solute concentration to area of higher solute
concentration. (For questions involving K+ and Ca++, think
electrical
status.)
2. Step by step process in understanding how a certain disease/disorder/situation/scenario cause fluid shifts: Remember that (for
our purposes) changes in fluid status
begin
in the plasma space. So in any scenario you are given:
STEP 1 is to think: “
How has this scenario changed the concentration in the plasma space
(
ie, blood concentration
)?”
o Has water been added to the blood or protein taken away (making the plasma space
less
concentrated)?
o Or has water been taken away from the blood (making the plasma space
more
concentrated)?
Also remember that the tissue fluid concentration status (cells and interstitial space)
remains normal initially
—the “normal”
number of solutes & “normal” amount of water exist in the tissue at the beginning of the scenario. When the plasma
concentration changed, it became either
more
concentrated or
less
concentrated than the normal tissue concentration.
STEP 2 is to think:
“The plasma concentration has changed to be either more or less concentrated than the tissue. I now have
to figure out what happens next
,
based on the principle of osmosis
(CONCENTRATION CALLS!)—
which way will fluid go? Tissue
to blood (blood more concentrated—“calls” fluid into it)? Or blood to tissue (blood less concentrated, so tissue “calls” fluid)?”
STEP I: The scenario resulted in water taken away
from plasma space. The blood is now _____
concentrated than it was & therefore _____
concentrated than the tissue fluid.
Tissue has normal
concentration.
Normal tonicity of tissue fluid
(interstitial fluid + ICF) is same or
near-same as blood. Fluid flow
between compartments is based
on small, balanced changes
throughout the day.
EX: Normal tonicity in plasma
space (blood) is 0.9% NaCl
The changed, pathologic situation will
always be one of these two scenarios:
Homeostasis: normal, “every-day”
status is that fluid compartments
throughout body have essentially the
same concentration most of the time.
Pathologic scenario A:
STEP 2:
which way
will fluid go: T to B
or B to T? _______
Pathologic scenario B:
STEP I: The scenario resulted in water added to
OR
protein taken from plasma space. The blood
is now ____ concentrated than it was & therefore
_____concentrated than the tissue fluid.
Tissue has normal
concentration.
STEP 2:
which way
will fluid go: T to B
or B to T? _______
B
B
B
T
T
T