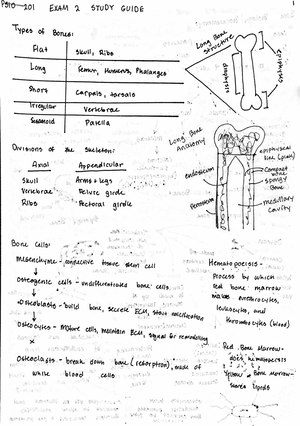
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Copy of Hemodynamic Monitoring
Course: Human Anatomy And Physiology I (PSIO 201)
179 Documents
Students shared 179 documents in this course
University: The University of Arizona
Was this document helpful?

Hemodynamic Monitoring
Clinical Manifestations &
Vitals
- tachycardia
- hypotension
- dyspnea
- change in LOC
- anxiety/ restlessness
- pallor, cool skin which can
advance to cool, clammy skin
- diminished pulses
- little or no urine output
- hypoactive bowel sounds
- decreased cardiac output
- decreased oxygen saturation
- hypoxemia
Pathophysiology and Terminology
Hemodynamic monitoring is the measurement of pressure, flow, and oxygenation within
the cardiovascular system.
-preload: volume within the ventricle at the end of diastole
-afterload: refers to the forces opposing ventricular ejection
-contractility: strength of the contraction
-cardiac index: measurement of the cardiac output adjusted for body surface area
-systemic vascular resistance: opposition to blood flow affecting LEFT ventricle
-pulmonary vascular resistance: opposition to blood flow affecting RIGHT ventricle
-central venous pressure: measurement of right ventricular preload
-pulmonary artery wedge pressure: measurement of pulmonary capillary pressure
Nursing Management
Monitor:
- general appearance
-LOC
- skin color and temp
- vital signs
- peripheral pulses
- capillary refill
- urine output
- lung sounds
- ECG
- bowel sounds
- reverse Trendelenburg
Interventions & Treatment
- two large bore IVs
- fluid resuscitation (not done with
cardiogenic shock)
- supplemental oxygen
- indwelling foley catheter and urometer
-NG tube
- FFP/ PRBC
- vasopressors
- steroids
- antibiotics
- nutrition
- treatment of underlying cause for
hemodynamic imbalance
Trending Labs:
- increase creatinine
- increase glucose
- increase lactic acid
- decrease hemoglobin and
hematocrit with hypovolemic
shock
- increase WBC (neutrophils) if
septic shock
- metabolic acidosis
- Monitor: K, Na, serum protein,
albumin, cultures
Hemodynamics of Shock
-Hypovolemic shock: decrease in PAWP (preload)
-Cardiogenic shock: decrease in cardiac output
-Distributive shock: decrease in SVR (afterload)