- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Gen Chem 1 Notes
Course: General Chemistry I (CHM2045)
268 Documents
Students shared 268 documents in this course
University: University of South Florida
Was this document helpful?

Gen Chem 1 Notes
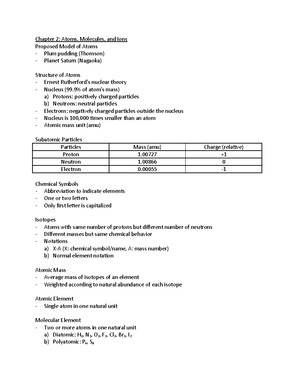
2.4 Chemical Bonds
- compounds: a substance composed of two or more elements in a fixed, definite proportion
- compounds are composed of atoms held together by chemical bonds, which result from the
attractions between the charged particles
2.4 representing compounds: chemical formulas and molecular models
- chemical formula indicates the elements present in the compound and the relative number of
atoms or ions of each.
- chemical symbol for each element
- subscript: number of atoms or ions (omit “1”)
2.4 types of chemical formulas
- chemical formulas can generally be categorized into two different types:
1. empirical formula gives u the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element ina
compound. (simplified version of molecular formula)
2. molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a
compound.
Elements that exist as molecules
- Diatomic molecules: H2, N2, O2, F2, CL2, Br2, I2
- The most common form of elemental sulfur exists as S8
- BrINIHOF
2.5 The period table
- Dimitri Mendeleev in Russia and Lothar Meyer in Germany independently recognized that
there was a periodic relationship among the properties of the elements known at that time.
Example: Lithium, sodium, and potassium are all shiny, conduct heat and have similar chemical
properties
2.5 the modern periodic table
- periodic law: the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
- a modern periodic table arranges the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers
and groups atoms with similar properties in the same vertical column
- periods or series: horizontal rows