- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Evaluating the Understanding of the Teaching for a Client Who Has Heart Failure system disorder
Course: Nursing (102)
190 Documents
Students shared 190 documents in this course
University: Verve College
Was this document helpful?

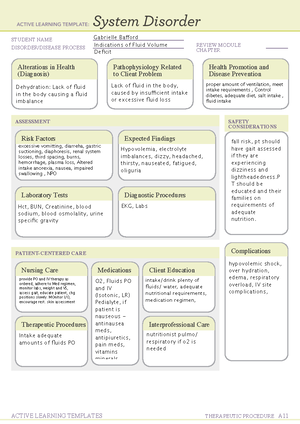
STUDENT NAME
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS REVIEW MODULE
CHAPTER
Alterations in Health
(Diagnosis)
Pathophysiology Related
to Client Problem
Health Promotion and
Disease Prevention
ASSESSMENT
Risk Factors Expected Findings
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE
Nursing Care
Therapeutic Procedures
Medications Client Education
Interprofessional Care
SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
Complications
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A11
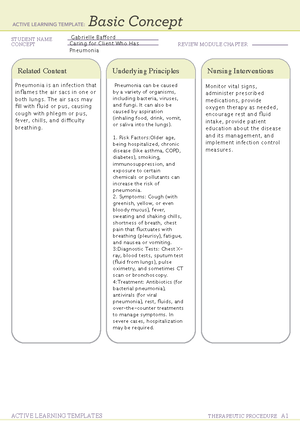
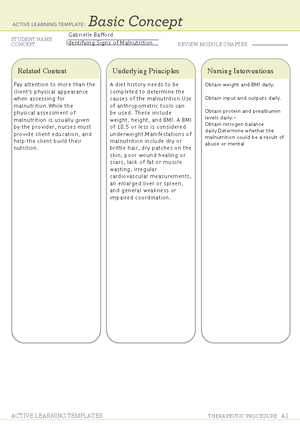
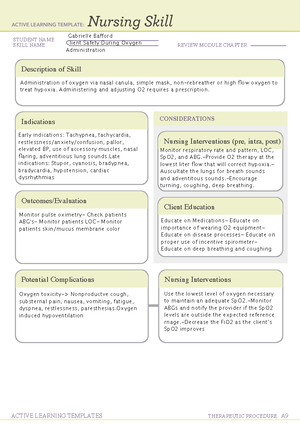
Gabrielle Bafford
Evaluating the Understanding of the
Teaching for a Client Who Has Heart
Failure
Result of an acute of chronic
cardiopulmonary problem.
The heart muscle is unable to pump
effectively, resulting in inadequate
cardiac output, myocardial
hypertrophy, and pulmonary/
systemic congestion
Maintain an exercise routine to remain
physically active and consult with
provider before starting any exercise
regimenconsume a diet low in sodium
along with fluid restrictions and consult
with the profvider regarding diet
Older adults have an increased
risk for heart failure and can have
worse manifestations due to
increased systolic blood presure
and some medications
Hemodynamic monitoring - mixed venous oxygen
saturation is directly related to cardiac output. a
drop in SvO2 indicates worsening cardiac
functionUltrasound - used to measure the systolic
and diastolic functioning of the
heartTransesophageal echocardiagraphy. Gives a
detailed view of cardiac structures
Fall Risk,Risk of
infection
Human B-type natriuretic peptides
(hBNP) elevated hBNP confirms a
diagnosis of heart failure in clients who
have dyspnea and rules out respiratory
illnesses
Dyspnea, orthopnea, nocturnal dyspnea,
fatigue, displaced apical pulse, frothy
sputum, pulmonary congestion, jugular vein
distention, ascending dependent edema,
weight gain, polyuria, nocturia
Monitor daily weight and I/Os assess
forshortness of berath and dyspnea on
exertion administer oxygen as
prescribed monitor vital signs and
hemodynamic pressures position the
client to maximize ventiliation
Diuretics -
furosemideAft
erload
reducing
agents - ACE
inhibitorsInotr
opic Agents -
digoxinBeta
blockers -
carvedilolVaso
dilators -
nitroglycerin
Use techniques to promote effective
breathing techniques understand
prescribed medications and how to
administer them continue to take
medications even if feeling better
follow instructions for reasons to
contact the provider remain on low-
sodium diet.
Acute pulmonary
edema
Cardiogenic shock
Pericardial
-tamponade
Pulmonary edema
Cardiology and pulmonary
servicesRespiratory services for
inhalers, breathing treatments, and
suctioningCardiac rehab for prolonged
weakness and assistance with
increasing level of activityNutrition for
diet modification
Ventricular assist device - a mechanical
pump that assists a heart that is too weak to
pump blood through the body used in
clients who are awaiting heart transplants or
who have severe end-stage heart
failure.Heart transplant- a possible option
for end-stage heart failure
Students also viewed
- Compre 1 Pharmacology Notes PN Prog
- Weekly Clinical template Blank N101
- Priority Findings for a Client Who Has Chronic Kidney Disease system disorder
- Preventing Infection Transmission of Clostridium Difficile Basic concept
- Ethical responsibilities Basic concept
- Promoting a Therapeutic Environment for Sleep Basic Concept
Related documents
- Nursing Responsibility When Obtaining informed conset basic concept
- Basic concept Caring for a Client Who is Postoperative Following Abdominal Surgery
- Basic Concept client that can provide informed consent
- Postoperative Care Following Mastectomy Basic concept
- Care of a closed suction drain system
- Bulimia Nervosa-Patience Mc Cormick