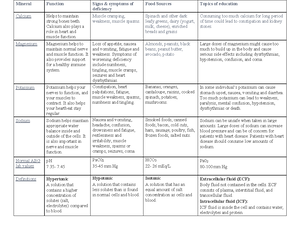
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
NSG 221 HESI Blueprint
Course: NSG med surg (NSG 223)
9 Documents
Students shared 9 documents in this course
University: West Coast University
Was this document helpful?

NSG 221 HESI Blueprint
Pre-test Items Not Graded
Abuse- question
Addiction- motivation to change
Addiction- relapse
Alcohol withdrawal- action
Heroin- history
Anxiety- panic
OCD- referral
PTSD- document
Antipsychotic- POC
Aggression- communication
Module 1
Counter transference- Countertransference occurs when the therapist displaces onto
the client attitudes or feelings from his or her past. For example, a female nurse who has
teenage children and who is experiencing extreme frustration with an adolescent client
may respond by adopting a parental or chastising tone. The nurse is countertransfering
her own attitudes and feelings toward her children onto the client.
Defense Mechanism- Freud believed that the self, or ego, uses ego defense
mechanisms, which are methods of attempting to protect the self and cope with basic
drives or emotionally painful thoughts, feelings, or events.
Therapeutic Milieu- planning- The concept of milieu therapy, originally developed by
Sullivan, involved clients’ interactions with one another, including practicing
interpersonal relationship skills, giving one another feedback about behavior, and
working cooperatively as a group to solve day-to-day problems.
Sleep Deprivation- Maslow (1954) formulated the hierarchy of needs, in which he used a
pyramid to arrange and illustrate the basic drives or needs that motivate people. The
most basic needs—the physiologic needs of food, water, sleep, shelter, sexual
expression, and freedom from pain—must be met first.
Tardive Dyskinesia- severe, late side effect of antipsychotic medication- permanent
involuntary movement
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome- med- dantrolene (muscle relaxant), bromocriptine
(dopamine stimulator), diazepam (benzo depressant)
Module 2
Civil rights- psychiatric patients- Clients receiving mental health care retain all civil rights
afforded to all people except the right to leave the hospital in the case of involuntary
commitment. They have the right to refuse treatment, to send and receive sealed mail,
and to have or refuse visitors. Any restrictions (e.g., mail, visitors, clothing) must be
made for a verifiable, documented reason. These decisions can be made by a court or a
designated decision-making person or persons, for example, a primary nurse or
treatment team, depending on local laws or regulations.
Refusal of treatment- Clients admitted to the hospital voluntarily have the right to leave,
provided they do not represent a danger to themselves or others. They can sign a
written request for discharge and can be released from the hospital against medical