- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
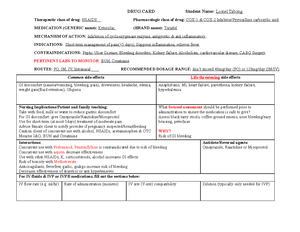
Pharm ATI #12 - Neal
Course: Pharmacokinetics and Medication Administration (NURS 205)
73 Documents
Students shared 73 documents in this course
University: Widener University
Was this document helpful?

IV
Therapy
and
Peripheral
Access
Isotonic
solutions
~
have
the
same
effective
osmolality
as
body
fluids
-
expand
intravascular
volume
Hypotonic
solutions
-
have
an
effective
osmolality
less
than
body
fluids
-
expand
the
intracellular
space
Hypertonic
solutions
-
have
a
greater
osmolality
than
body
fluids
-
infused
to
treat
clients
who
have
severe
hypoatremia
clients
who
can
benefit
from
midline
catheters
-
clients
who
have
limited
peripheral
veins
-
altered
peripheral
skin
integrity
-
longer
term
Iv
antibiotics
-
heparin
infusions
for
DVT
-
repeated
steroid
infusions
Interventions
that
should
not
be
conducted
on
midline
catheters
-
Parenteral
nutrition
-solutions
with
osmolarity
greater
than
600
mosm/
-
routine
blood
draws
-
incompatible
medication
administration
via
dual
lumen
catheters
circulatory
overload
-
a
systemic
complication
of
IV
therapy
that
causes
excess
fluid
in
the
circulatory
system