- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
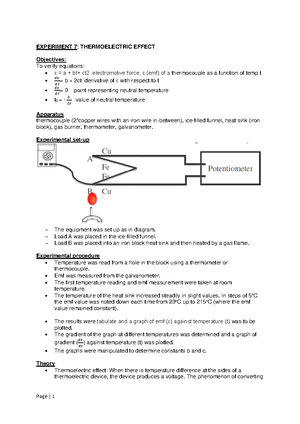
Steady-state and transient responses
Course: Process Control Systems 3B
22 Documents
Students shared 22 documents in this course
University: Durban University of Technology
Was this document helpful?

Steady-state and transient responses
Transient response + Steady-state response = Total response
Transient response definition:
The transient response is that part of the total response which decays with time and eventually
vanishes as time approaches infinity.
The characteristics of the transient response of a system, are usually defined on the basis of a
step input.
Steady-state response definition:
The steady-state response is that part of the total response which persists indefinitely as time
approaches infinity.
Consider the function: f(t) = 2e 2t + t - 3;
The term, 2e 2t , decays with time but the term t - 3, persists indefinitely.
Unfortunately, there is always an error involved in the steady-state performance and ways of
minimising this steady-state error, is discussed in paragraph 3.4.17.
3.4.2 Singularity functions: steps, ramps, and impulses
In the study of control systems and the equations which describe them, a particular family of
functions called singularity functions is used extensively. Each member of this family is related
to the others by one or more integrations or differentiations. the three most widely used
singularity functions are the unit step, the unit impulse, and the unit ramp.
A unit step function I(t - to) is defined by