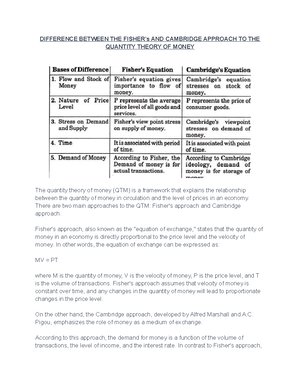
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
IBRD - This file contains the notes on IBRD.
Course: Economics
999+ Documents
Students shared 1436 documents in this course
University: University of Calcutta
Was this document helpful?

THE INTERNATIONAL BANK FOR RECONSTRUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) is a specialized
agency of the United Nations that provides loans and technical assistance to developing
countries. Here are some key points to note about the IBRD:
1. History: The IBRD was established in 1944 as part of the Bretton Woods
Conference, which created the post-World War II international financial
system. Its primary goal was to help rebuild Europe and provide development
assistance to developing countries.
2. Membership: The IBRD has 190 member countries, with the largest
shareholders being the United States, Japan, and China. Membership is open
to all countries that are members of the United Nations or its specialized
agencies.
3. Purpose: The IBRD’s primary purpose is to provide loans and technical
assistance to developing countries for projects that promote economic
development, reduce poverty, and improve living standards. It provides
financing for projects in sectors such as infrastructure, health, education, and
the environment.
4. Financial Structure: The IBRD is a self-sustaining financial institution and
raises funds from capital markets by issuing bonds. Its financial strength is

![Economic and social development by mk yadav [@Upsc Pdf Drive]](https://d20ohkaloyme4g.cloudfront.net/img/document_thumbnails/6b976e52e96da8533c772a157831f7b5/thumb_300_424.png)