- Information
- AI Chat
Tutorial Sample CTs
Auditing (AUD339)
Universiti Teknologi MARA
Recommended for you
Related Studylists
AUD339Preview text
SOLUTION TEST 1 AUD339 (APRIL 2021, OCTOBER 2019 & APRIL 2019)
FOR LEARNING PURPOSES
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION
OCT
Identify the type of audit applicable in the following situation:
No Type of audit i. Compliance audit ii. Operational audit iii. Financial Statement audit iv. Compliance audit
APR
i) Government auditor ii) Internal auditor iii) External auditor iv) Forensic auditor
OCT
No Types of audits Types of Auditors i. Financial Statement audit External auditor ii. Financial Statement audit External auditor iii. Compliance audit Internal auditor iv. Operational audit Internal auditor
NOV
i) Forensic audit ii) Financial statements audit iii) Operational audit iv) Compliance audit
JAN
Situation Types of audits Types of Auditors i. Operational audit Internal auditor ii. Compliance audit Government auditor iii. Forensic audit Forensic auditor iv. Financial statement audit External auditor
APRIL 2021
QUESTION 1
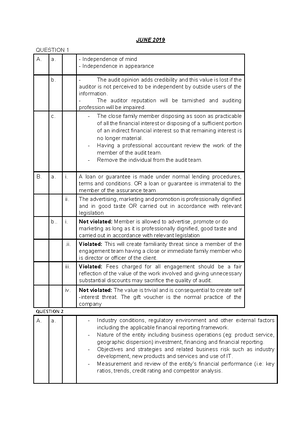
a. Define: (i) Independent examination: using audit procedures and carrying out tests to accumulate self-generated evidence, third-party evidence, which are independent from management before arriving at the conclusions on which the audit opinion is based. (ii) Communicating results: to be useful, the results of the audit need to be communicated to interested parties by either oral or written means.
b. An agency relationship arises when one or more principals (owner) engage another person as their agent (or steward) to perform a service on their behalf. Agents are likely to have different motives to principals. They may be influenced by factors such as financial rewards, labour market opportunities, and relationships with other parties that are not directly relevant to principals. As a result of these differing interests, agents may have an incentive to bias information flows and creates information asymmetries. Principals may also express concerns about information asymmetries where agents are in possession of information to which principals do not have access. An audit provides an independent check on the work of agents and of the information provided by an agent, which helps to maintain confidence and trust.
c. Yes. It is important for the auditor to understand management’s motivation to misstate financial statements because helps the auditor to identify the financial statement accounts with the most potential for misstatement and to design audit procedures to determine and to give assurance that the accounts are fairly presented according to the applicable financial reporting framework.
d. Four reasons for the growing demand on auditing (i) Complexity of business environment. (ii) Growing size of business entity. (iii) Conflict interest on the part of agents or management. (iv) Users of financial information expectation and agents does not match.
QUESTION 2
a) Benefits of an audit performed by an external auditor: An audit performed by an external auditor would ensure that the opinion issued to the shareholders is free from bias and is highly reliable because it is issued by a competent and independent party that has no relationship with the management of the company.
b) Absolutes are not attainable due to factors such as the need for professional judgment, the use of testing, the inherent limitations of internal control, the reliance in accounting on estimates, and the fact that audit evidence is generally persuasive rather than conclusive. Moreover, audit is done based on audit sampling that tested on the percentage number of transaction and not the whole population. Reasonable assurance is measure of the level of uncertainty that the auditor has obtained at the completion of the audit that indicates the auditor is not insurer or guarantor of the correctness of the financial statement.
d. THREE (3) reasons for casual vacancy: i. Death of the auditor ii. Removal of auditor iii. Resignation of auditor
e. Situation Violated/Not violated Reasons i. Violated The amount of outstanding debt is RM56,000 which is more than the threshold of RM25,000, violate the S (1) (c) (ii). ii. Not violated Although Azalea’s husband is the Chief Accountant, but Azalea is not involved with the engagement, thus not violate the CA 2016. iii. Violated The firm falls under S (iv) - responsible for the keeping of the register of the member or register of the debenture holders of the company thus cannot be appointed as the auditor. iv. Violated Auditor has right to access any books and records he deemed necessary and relates to the audit engagement based on S (4).
OCTOBER 2019
QUESTION 1
a. Briefly explain the following keywords from the above definition: i. Independent examination Using audit procedures and carrying out tests to accumulate evidence which are independent from management before arriving at the conclusions on which the audit opinion is based.
ii. Appointed auditor An approved company auditor or the audit firm ranges from sole proprietorships to partnerships providing broad categories of services such as attestation services including audits, tax services, accounting service and management advisory services.
b. THREE (3) functions of the Malaysian Institute of Accountant (MIA) in regulating the profession: - To regulate the accounting profession in Malaysia. - To review accounting and related practice for Malaysian Accountant. - To issues guidelines for accountant. - To conduct research on the accounting professions.
c. Any TWO (2) regulatory requirements that helps to regulate an auditing process and profession in Malaysia. - Malaysian Approved Standards on Auditing (MASA) - Malaysian institute of Accountants (MIA) - Companies Act 2016
d. THREE (3) factors that lead to the demand for auditing: - Complexity of business environment. - Users of financial information expectation and agents does not match. - Conflict of interest on the part of agent’s management.
- Growing size of business entity.
e. THREE (3) responsibilities of management relating to financial statements: - Preparation of annual financial statements. - Maintaining adequate accounting records and internal control. - Apply appropriate accounting policies. - Safeguard of company’s assets.
QUESTION 2
a. THREE (3) reasons for the auditor to provide reasonable assurance rather than absolute assurance: (i) Most audit evidence results from testing a sample of population. (ii) Accounting presentations enclose complex estimates, which involve uncertainty & can be affected by future events. (iii) Fraud is extremely difficult or impossible to detect.
- Power to directors to appoint auditor to fill any casual vacancy (termination of business-winding up cases, etc.), except for dismissal or removal.
c. The process for resignation of auditor as prescribed under Section 281 and 282 of the Companies Act 2016. - An auditor may resign by giving notice to the company at the registered office. - The auditor shall within 7 days of serving such notice, submit to SSM his reason for resignation. - The company need to send a copy of resignation notice to SSM within 7 days of receipt. - Resignation of auditors shall be valid within 21 days of serving the notice at the registered office.
B. State whether the following situations violate the Companies Act 2016 requirements.
Situation
Violated/Not Violated Reason
a. Violated
S – A person is disqualified to become an approved company auditor if he or she is an officer of the company.
b. Not violated
S(7) – An auditor has a power to attend any general meeting and to receive all communications relating to any general meeting which may concern the auditor in his capacity as auditor.
c. Violated
S – The remuneration of an auditor shall be fixed by a person who appointed the auditor, e. if appointed by members, the remuneration shall be fixed by the members.
d. Not violated
S – This section allows the BOD to appoint an approved company auditor to fill casual vacancy.
e. Violated
S – The act requires special notice of at least 28 days to be given by shareholders for removal of auditors.
Notes: What is approved company auditor? Related to approved company auditor. Company Auditor means the independent registered public accounting firm responsible for conducting the audit of the Company's annual financial statements.
The laws in Malaysia also require that a company's annual audit must be performed by an approved company auditor or audit firm. An approved auditor in Malaysia is a person approved by the Ministry of Finance.
The Ministry may, if he is satisfied that the person is of good character and competent to perform his duties as a company auditor, approve the person as company auditor in Malaysia. The Ministry will grant an audit license for approved auditors in Malaysia, which is renewable every 2 years.
A partnership firm of auditors in Malaysia may be appointed as auditors in the firm's name. In practice, most of the appointments of auditors in Malaysia are in the name of the audit firm. Every partner of the audit firm in Malaysia must individually be an approved company auditor.
Tutorial Sample CTs
Course: Auditing (AUD339)
University: Universiti Teknologi MARA

- Discover more from: