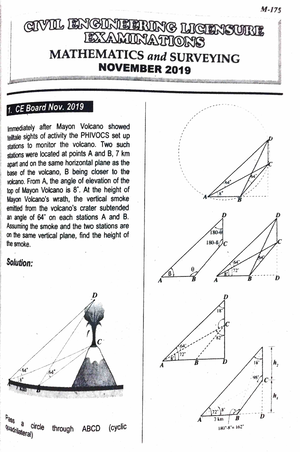
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Calomitry experiment
Course: Civil Engineering
999+ Documents
Students shared 2987 documents in this course
University: Bicol University
Was this document helpful?

Calorimetry
Jhon Armand M. Hermonda
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of San Carlos
polbox789@gmail.com
Abstract
This report is about Calorimetry in where it carried out to determine whether reaction is
endothermic or exothermic using temperature changes observed and carry out determination of
the heats of the reaction using an improvised calorimeter. 3 types of experiment were done,
determination of the calorimeter constant, heat of solution, and determination of heat of
neutralization. The 1st experiment was an improvised calorimeter was used which is a Styrofoam
coffee cups, a cold water was put inside it followed by a distilled water after 3 minutes of
boiling, then calculate the heat changes. The 2nd experiment was an ammonium chloride in
distilled water put in the improved calorimeter and was to determine if it is endothermic or
exothermic. The last experiment was a Hydrochloric acid mixed in Sodium Hydroxide after the it
is done, calculation was done to find the heat that flowed from the reaction into the water of the
reactant solution or vice versa, the number of moles of each reactant and the number of moles of
each product and the change of heat in terms of kilojoules per mole. The experiments done
exhibits experience of errors in the process and close and far percent of error from the theoretical
value.
Introduction
During the events in which physical changes and chemical reactions take place, energy
changes also always occur alongside it, which is observed as the heat flow into or out of the
system. An endothermic process requires the absorption of heat, while an exothermic process
releases heat.
The measurement of heat changes in physical and chemical processes is called calorimetry, in
which the heat flow for a process is measured with the use of an instrument known as
calorimeter. To prevent heat loss or gain between the instrument and its surroundings, the
calorimeter is insulated. A weighed amount of water which serves as the heat sink is contained,
and monitoring of the water’s temperature is done when the process involving the study is
performed within the calorimeter. The quantity of heat transferred by the process is determined
from the mass of water in the calorimeter and the changes in the water’s temperature.
To calculate the quantity of heat energy that transfers during the physical or chemical
process, the values of the temperature changes undergone by the water are used. The quantity of
heat which is involved in the temperature change, Q, is given by the following formula:
Q = mCΔT
where m is determined as the mass of the water, C is the specific heat of water (4.18 J g-
1C-1), and ΔT represents the change in temperature.