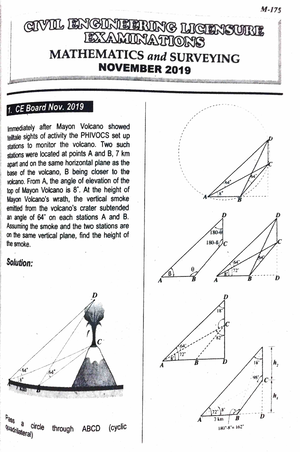
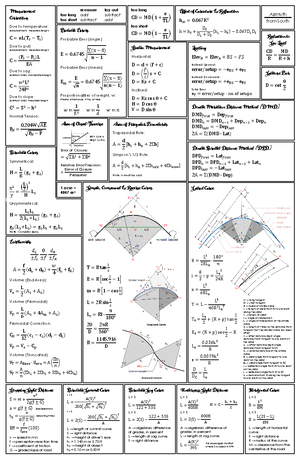
- Information
- AI Chat
PRAC RES 2 editor copy
Civil Engineering
Bicol University
Recommended for you
Preview text
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
ATTITUDES AND PRACTICES OF SHS STUDENTS TOWARDS SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT AT NDMU
A Quantitative Research Presented to the Faculty of Senior High School Department Notre Dame of Marbel University Koronadal City, South Cotabato In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements in PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
ADELANTAR, JOIEJE FAYE D.
BACONGCO, SYLPH RENAEMY B.
DIME, JOSHUA CHRISTOPHER C.
FRANCISCO, EPHRAIM JAY V.
LAZARITO, REZEILE JOHN F.
Grade 12 – STEM 7
ANALYN M. CABATINGAN, PhD Research Adviser
FEBRUARY 2019
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The researchers would like to convey their heartfelt gratitude for the support, inspiration and guidance of the following persons for the successful completion of this study. Firstly, we would like to thank our Almighty Father for giving us the strength, knowledge and wisdom to finish our study successfully, and for without Him, we could have not succeded with this endeavor. To our Practical Research 2 adviser, Mrs. Analyn M. Cabatingan for being with us all throughout the making of this research. To our Parents, Mr. & Mrs. Adelantar, Mr. & Mrs. Bacongco, Mr. & Mrs. Dime, Mr. & Mrs. Francisco, Mr. & Mrs. Lazarito we are very thankful for their unending support and guidance from physical presence to financial help, and for being with us until we finished our research. To our Principal, Mrs. Leann Jester Daus – Rosali for approving our study and for letting us conduct the survey. And lastly, to the respondents who answered and participated to our survey. We could have not done this without their humble participation.
i
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department ABSTRACT This study aimed to assess the attitudes and practices of Senior High School Students of Notre Dame of Marbel University towards solid waste management. It utilized a descriptive-quantitative study. The first statemement of the problem is to determine the profiles of the respondents in terms of their age, sex, grade level and strand. Next, how to determine the attitudes of SHS students towards solid waste management in terms of waste generation, waste storage, waste collection, waste transfer and transport, waste processing and waste disposal. Lastly, how SHS students practice towards solid waste management in terms of waste generation, waste storage, waste collection, waste transfer and transport, waste processing and waste disposal. Majority of the respondents were in the age range of 20 years old and below, more specifically 15 years old to 20 years old and more than half of the respondents are female and the rest are male. In terms of the attitudes of the respondents towards solid waste management, majority of them would throw their garbages on the trash bin and they are aware of the negative effects of garbage in the environment and in the human body. They are also willing to improve the proper disposing of garbage through following rules and regulations. The researchers rate that mostly of the the respondents have a proportional answer about the relationship between the attitudes and practices of each respondents towards solid waste management. Each of the respondents has an
iii
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
attitude on how to dispose properly their own garbage and would like to practice it consistently. The respondents’ practices in solid waste management specifically answered agree which means they have a positive attitude and from the questionnaire, they would prefer to pick up trashes and throw it in the trash bins and got a higher percentage. Meanwhile, the transferring and transporting of the collected garbage to the dumping site need to address by the administration which is moderately and fairly practiced, according to the respondents. Overall, the Senior High School Students of Notre Dame of Marbel University are aware and have the knowledge on/in solid waste management.
iv
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research Design......................................................... 20 Research Paradigm ...................................................... 21 Locale of the Study......................................................... Research Instrument...................................................... Research Respondents................................................. 24 Data Collection Procedure............................................... 25 Data Analysis................................................................ CHAPTER IV. PRESENTATION OF ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA Profile of the Respondents................................................ 28 Significant Difference of students in terms of Age................... Significant Difference of the students in terms of Sex.............. Significant Difference of the students in terms of Grade Level.... Significant Difference of the students in terms of Strand........... Attitudes of the Respondents towards SWM.......................... Practices of the Respondents towards SWM ......................... CHAPTER V. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION, AND RECOMMENDATION Summary of the Finding.................................................. 48 Conclusion.................................................................. 50
v
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
Recommendation.......................................................... 50 REFERENCES............................................................................. CURRICULUM VITAE................................................................... vi
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
LIST OF TABLES
- 1 Research Respondents.......................................................... Table Title Page
- 2 Likert Scale on Solid Waste Management...................................
- 3 Percentage Distribution of the Respondents in terms of Age..........
- 4 Percentage Distribution of the Respondents in terms of Sex...........
- 5 Percentage Distribution of the Respondents in terms of Grade Level
- 6 Percentage Distribution of the Respondents in terms of Strand.......
- 7 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste Generation..............
- 8 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste storage...................
- 9 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste collection................
- 10 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste transfer & transport....
- 11 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste processing................
- 12 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste disposal....................
- 13 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste generation...............
- 14 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste storage.....................
- 15 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste collection................
- 16 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste transfer & transport....
- 17 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste processing................
- 18 Mean Results of the Respondents on Waste disposal....................
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
19 Significant Difference on the Profile of the students in terms of Age .................................................................................................... 20 Significant Difference on the Profile of the students in terms of Strand........................................ 21 Significant Difference on the Profile of the students in terms of Sex ............................................... 22 Significant Difference on the Profile of the students in terms of Grade Level........................................
ix
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
Background of the Study One of the problem and challenges that each individual facing today is the issue of waste in society. Solid waste disposal and management is both rural and urban problem. Every person in the society is a potential generator of waste and this could worsen the increasing volume of waste. Waste is generated from different sectors in commercial, industry, food waste, animal manure, ashes, broken tools, utensils, old clothing, and others. Large volume of waste can cause pollution in water, soil, and in air. Pollution can all be a result of improper waste disposal and occurs when either of them becomes contaminated with hazardous materials. Not only does this contribute to the creation of a greenhouse gases effects but also causes significant harm to marine and wildlife. The waste that was dumped in the ocean by industrial waste companies, construction and demolition debris, and informal settlers is one of the huge contributor of waste and this would mean that the effects to the ocean is huge as well. According to an article written by (Ranada, 2015), the Philippines was ranked the 3rd top source of plastic leaking into oceans in a February 2015 study. The country generates 2 million metric tons of plastic garbage each year, 20% or 521,
xi
1
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
tons of which ends up in the ocean, and the world's third biggest dumper of plastic in the ocean (Suarez, 2015). The waste that was dumped in the ocean would tend to have toxic substances, which will penetrate the production of oxygen, with the lack of oxygen the marine life will tend to die in their natural habitat. A team of researchers in the United States and Australia led by Jenna Jambeck, an environmental engineer at the University of Georgia, analyzed plastic waste levels in the world's oceans. They found out that China and Indonesia are the top sources of plastic bottles, bags and other rubbish waste clogging up global sea lanes (McCarthy, 2018). Pollution could also a cause to various diseases that is very harmful in our body. Exposure to hazardous waste can affect our body, especially children being more vulnerable to different pollutants. Direct exposure can lead to diseases through chemical exposure as the release of chemical waste into the environment leads to chemical poisoning. According to an article by (Tomacruz, 2018), the Philippines are the third country having the highest number of deaths due to air pollution according to World Health Organization (WHO). Furthermore, Health experts urge the government to develop a plan to improve air quality as about 45 of 100,000 Filipinos die due to air pollution. Waste is one of the major causes of flood because of the blocked leakage in the canals. During rainy days the free flow of water that enters into the drains causing the water to back up during rainfall that will lead to flooding the
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
protection and things to follow to properly handle and manage our own waste, such activities like Model Class of the Week, Making Recycled Gowns, Environmental Robot, Trash Bin Painting and other environmental activities. Although the University practice these activities to lessen waste, but still these activities won’t eliminate the waste. Hence, it needs an appropriate management and disposal method to clearly reduce and eliminate the waste. The main objective of this study is to assess the knowledge about the attitudes and practices of senior high school students towards solid waste management at Notre Dame of Marbel University. Here, the researchers can see the explanations and will able to elucidate the different mechanism of how these types of entity contributes much to the solid waste management issue in general. The researchers could also find the right method and action to address these common problem that been causing too much trouble in our society.
Statement of the Problem This study aims to determine and describe the attitudes and practices of SHS students towards Solid Waste Management at NDMU:
- What are the profiles of the respondents in terms of: a. Age, b. Sex, c. Grade level, and d. Strand?
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
- What are the attitudes of SHS students towards Solid Waste Management in terms of: a. Waste Generation, b. Waste Storage, c. Waste Collection, d. Waste Transfer and Transport, e. Waste Processing, and f. Waste Disposal?
- What are the practices of SHS students towards Solid Waste Management in terms of: a. Waste Generation, b. Waste Storage, c. Waste Collection, d. Waste Transfer and Transport, e. Waste Processing, and f. Waste Disposal?
- Is there significant relationship between the attitudes and practices of the respondents towards Solid Waste Management?
4
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department To the Solid Waste Management Club, the given data would also help them how to improve and how to manage the proper waste segregation program that will help the school to improve in terms of solid waste management. For the future researchers, this study is beneficial to the future researchers, Research with the same study might use this as a guide in making their own research. Future researchers may get related literatures to support their research and they could modify what is/are missing in their research.
Scope and Delimitation In general, the focus of this study is directed towards the attitudes and practices of senior highschool students towards Solid Waste Management at Notre Dame of Marbel University. About 330 senior highschool students are the respondents selected in Notre Dame of Marbel University. The study is largely dependent on the honesty, sincerity and integrity of the respondents. The primary data gathering method used were questionnaires in order to determine the attitudes and the practices of senior highschool students towards Solid Waste Management in Notre Dame of Marbel University. This study considered every aspect of students’ personal information that has an impact on their academic performances. Each of the respondents is given the same questions to answer. The answer of the respondents that participated in this research will remain confidential.
6
Lungsod ng Koronadal, Timog CotabatoSenior High School Department
CHAPTER II
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK AND REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
Conceptual Framework The conceptual framework contains the specified goal of the statement of the problem. It includes the attitudes and practices of the student towards Solid Waste Management more specifically the waste generation, waste storage, waste collection, waste transfer and transport and waste processing. It also includes the profiles of the student which specifically are the age, sex, grade and section and Strand. All that is written are connected to one another. The conceptual framework contains all that is stated in the statement of the problem.
7
Attitude towards Solid Waste Management A) Waste Generation B) Waste Storage C) Waste Collection D)E) Waste Transfer and TransportWaste Processing Profiles F) Waste Disposal A) Age B) Sex C) Grade and Section D) Strand
Practices towards Solid Waste Management A) Waste Generation B)C) Waste StorageWaste Collection D) Waste Transfer and Transport E) Waste Processing F) Waste Disposal
PRAC RES 2 editor copy
Course: Civil Engineering
University: Bicol University

- Discover more from:Civil EngineeringBicol University999+ Documents
- More from:Civil EngineeringBicol University999+ Documents