- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
ART 9 Q1 Lesson Exemplar
Subject: BS Education
237 Documents
Students shared 237 documents in this course
School: Carigara National High School
Was this document helpful?

Lesson Exemplar in ARTS Using the IDEA Instructional Process
LESSON
EXEMPL
AR
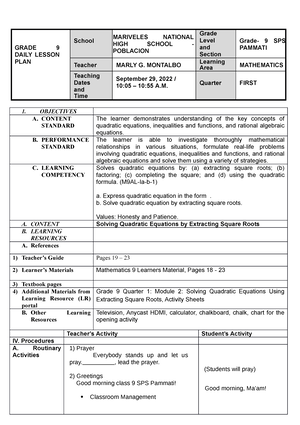
School DOLORES NATIONAL HIGH
SCHOOL
Grade Level GRADE 9
Teacher VIOLETA A. CASTILLO Learning Area MAPEH- Arts 9
Teaching Date
and Time
Quarter FIRST
I. OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson, learners are expected to:
1. Analyze art elements and principles in the production of
work following the style of a western and classical art.
2. Identify distinct characteristics of arts during the different
art periods.
3. Identify representative artists from various art
periods.
A. Content Standard Art elements and processes by synthesizing and applying prior
knowledge and skills
B. Performance Standard Perform / participate competently in a presentation of a creative
impression (verbal/nonverbal) of a particular artistic period
C. Most essential Learning
Competencies (MELC)
( If available write the indicated
MELC)
1. Analyzes art elements and principles in the production of work
following the style of a western and classical art A9EL-Ib-1
2. Identifies distinct characteristics of arts during the
different art periods A9EL-Ia-2 A9EL-Ia-2
3.Identifies representative artists from various art
periods A9EL-Ia-3
A9EL-Ia-3
D. Enabling Competencies
II. CONTENT WESTERN CLASSICAL ART TRADITION
Paintings from the Pre-historic
Paintings from the Ancient Egypt
Paintings from the Classical Greek Era
Paintings from the Romantic Era
Paintings from the Medieval
Paintings from the Greek Era
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
a. Learner’s Materials pp. 138-190
b. Teacher’s Guide Pages 177-178
c. Additional Materials from
Learning Resources
B. Additional Learning Resources
for Development and Engagement
Activities
IV. Procedures
INTRODUCTION
A. What I need to know?
The Teacher Ask the following introductory questions.
1. What are the elements and principles of art?
2. What are the different types of art forms?
3. How would you classify the different artworks into their
respective period?
4. What was your basis of classification?
5. Try to analyze each art form and discover how each
developed in every period.