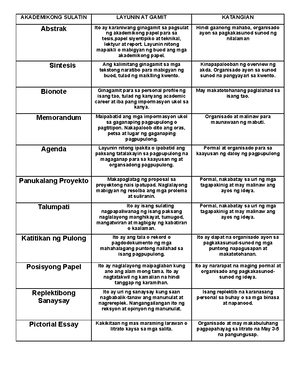
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Botany - This is for college students only. For bs Pharmacy students
Course: BS Secondary Education (DRRR 01)
999+ Documents
Students shared 3575 documents in this course
University: Cotabato State University
Was this document helpful?

JUNIMY MELCHOR GAMONGAN
BS PHARMACY 1
The five different activities performed by membrane proteins in multicellular organisms are
enzymatic functions, transportation, signal transduction, cell recognition and intercellular joining.
Enzymes in the membrane can do the same thing they do in the cytoplasm of a cell: transform a
molecule into another form. Anchor proteins can physically link intracellular structures with
extracellular structures. While, a membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane
protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another
protein, across a biological membrane. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by
facilitated diffusion or active transport. The signal transduction originates at the membrane, where the
clustering of signaling proteins is a key step in transmitting a message. The cell recognition proteins are
glycoproteins that have several functions, such as recognition of pathogens . These proteins serve as a
cell’s “identity badge”. If the cells of you immune system see a cell in your body that doesn’t have the
correct glycoproteins sticking out of it. While, intercellular junctions are specialized regions of contact
between the plasma membranes of adjacent cells. They are essential to any multicellular organism,
providing the structural means by which groups of cells can adhere and interact.