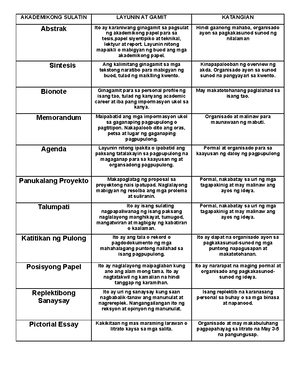
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Toaz - This is for SHS Literature subject
Course: BS Secondary Education (DRRR 01)
999+ Documents
Students shared 3575 documents in this course
University: Cotabato State University
Was this document helpful?

21st Century Literature from the Philippines and
the World
REVIEWER
What is LITERATURE?
- LITERATURE (origin of term – litera which
means letter) deals with ideas, thoughts, and
emotions of man – thus it can be said the
literature is the story of man. (Kahayon, 1998,
p.5-7);
- LITERATURE comes from the French phrase
<belles-letters= which means beautiful writings.
(Baritugo, et al. 1993, p.3)
- In its broadest sense, LITERATURE is
everything that has ever been written.
- Through LITERATURE, we learn the
innermost feelings and thoughts of people.
Why do people read LITERATURE?
- Information
- Amusement
- Higher and keener pleasure
- Cultural upliftment
- Discovery of broader dimensions in life
DIVISIONS OF LITERATURE:
PROSE and POETRY
PROSE
POETRY
FORM
Written in
paragraph
form
Written in
stanza or
verse form
LANGUAGE
Expressed in
ordinary
language
Expressed in
metrical,
rhythmical,
and figurative
language
APPEAL
To the
intellect
To the
emotion
AIM
To convince,
inform,
instruct,imitate
and reflect
Stir the
imagination
and set an
ideal of how
life should be
GENRES OF LITERATURE
I.PROSE: is expression (whether written or
spoken) that does not have a regular rhythmic pattern.
Prose does have rhythm but its rhythm lacks any
sustained regularity and is not meant to be scanned.
SUBTYPES OF PROSE
1.FICTIONS: are made up stories, imaginary things,
people, events and writing. Fiction tends to be focusing
on imaginary ideas and events.
Examples:
A. Fairy Tales – stories are about fairies or other
magical creatures, usually for children.
B. Fable – a story about supernatural or
extraordinary people. Animals often speak as
humans that are legendary and supernatural
tales.
C. Folklore – songs, stories, myths and proverbs of
a person of <folk= that was handed down by
word of mouth.
D. Science Fiction – is a story based on impact of
potential science, either actual or imagined.
E. Mythology – a type of legend or traditional
narrative. This often based in part of historical
events that reveals human behavior and natural
phenomena by its symbolism; other pertaining to
the actions of gods
2.NONFICTIONS: involve real things, people,
events, places and writing. Non-fiction focuses on ideas
or events that actually took place.
Examples:
A. Essays – a short literary composition on a
particular theme or subject, usually in prose and
generally analytic, speculative or interpretative.
B. Biography – is a written account of another
person’s life.
C. Autobiography – gives the history of a person’s
life.
D. Speech - the faculty or power of speaking; oral
communication, ability to express one’s thoughts
and emotions.
II. POETRY: is expression that is written in verse,
often with some form of regular rhythm. The basis of
poetic expression is a heightened sense of perception or
consciousness.
SUBTYPES OF POETRY
a. Lyrical Poetry: a verse or poem that is
susceptible of being sung to the accompaniment
of a musical instrument.
b. Narrative Poetry: a form of poetry that tells a
story, often making the voices of a narrator and
characters as well; the entire story is usually
written in metered verse
c. Dramatic Poetry: any drama that is written in
verse that is meant to be recited.
• Literature can ALSO be classified into five
categories or genres:
• 1. Prose Fiction - imaginary stories
• 2. Poetry – is an expression that is written in
verse, often with some form of regular rhythm.
• 3. Drama- is designed to be acted out on a stage
performed by actors in front of the audience.
The two broad categories of drama are Comedy
and Tragedy.
• 4. Nonfiction Prose – any kind of prose writing
that is based on facts.
• 5. Creative Nonfiction- uses literary styles and
techniques to create factually accurate narratives
What is PHILIPPINE LITERATURE?
<…the literature associated with the Philippines and
includes the legends of prehistory, and the colonial
legacy of the Philippines, written in both indigenous, and
Hispanic languages.=
TIMELINES IN PHILIPPINE LITERATURE
Pre-Colonial Times
- The longest period in Philippine Literatures.