- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Biochem Midterms
Course: BIOCHEMISTRY (CHM3)
365 Documents
Students shared 365 documents in this course
University: Our Lady of Fatima University
Was this document helpful?

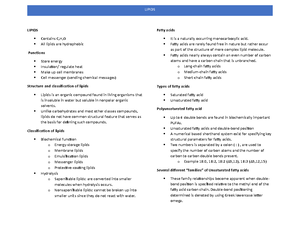
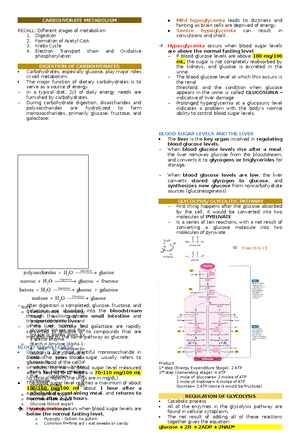
BIOCHEMISTRY WEEK 8
METABOLISM ENERGY PRODUCTION
Biochemical energy is the energy stored in organic and living matter.
The primary energy-releasing pathways of metabolism involve the breakdown and
synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids. Energy Flow in the Biosphere Energy
is transferred between organisms in food webs from producers to consumers. The energy
is used by organisms to carry out complex tasks. The vast majority of energy that exists in
food webs originates from the sun and is converted (transformed) into chemical energy by
the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Producer→ Primary Consumer→ Secondary Consumer→ Apex (Tertiary Consumer)
CELL STRUCTURE MITOCHONDRIA are membrane-bound cell organelles that generate
most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions Functions
of the Mitochondria
1. Regulates the metabolic activity of the cell
2. Promotes the growth of new cells and cell multiplication
3. Helps in detoxifying ammonia in the liver cells
4. Plays an important role in apoptosis or programmed cell death
5. Responsible for building certain parts of the blood and various hormones like
testosterone and estrogen
6. Helps in maintaining an adequate concentration of calcium ions within the
compartments of the cell
7. It is also involved in various cellular activities like cellular differentiation, cell signaling,
cell senescence, controlling the cell cycle and also in cell growth CYTOPLASM Cytoplasm
is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts,'and
various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and
mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm.
Function of Cytoplasm
1. The cytoplasm is home to many activities of the cell as it contains molecules, enzymes
that are crucial in the break down of the waste.
2. The cytoplasm also assists in metabolic activities.
3. Cytoplasm provides shape to the cell.