- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Week 10-Nucleic Acids
Course: BIOCHEMISTRY (CHM3)
365 Documents
Students shared 365 documents in this course
University: Our Lady of Fatima University
Was this document helpful?

BIOCHEMISTRY FOR MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE (CHEM113lec)
Lecture by: Mr. Joseph Deuel Casinsinan | Transes made by: Nicole Maranan
Please do not distribute the transes, especially w/o permission of the owner.
Week 10: Nucleic Acids
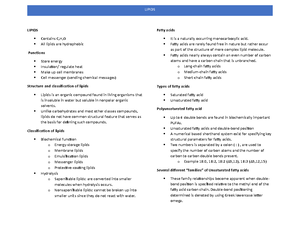
Nucleic Acid
- a polymer in which the monomer units
are nucleotides.
Types of NA:
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) – nearly
all DNA is found within cell nucleus;
primary function is storage and
transfer of genetic information
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)- for synthesis
of proteins
Nucleotide
- Building blocks of
NA
- Three-subunit
molecule in which
a pentose sugar is bonded to both a
phosphate group and a nitrogen-
containing heterocyclic base
Pentose Sugars
- The sugar unit of a nucleotide is
either the pentose ribose or the
pentose 2’-deoxyribose
- RNA and DNA differ in the identity of
the sugar unit in their nucleotides. In
RNA the sugar unit is ribose-hence the
R in RNA. In DNA the sugar unit is 2’-
deoxyribose-hence the D in DNA
Nitrogen-Containing Heterocyclic Base
- Five nitrogen-containing heterocyclic
bases are nucleotide components.
- Three of them are derivatives of
pyrimidine (six membered ring) and
two are derivatives of purine (bicyclic
base with fused five- and six-
membered rings).
- Both of these heterocyclic compounds
are bases* because they contain
amine functional groups, and amine
functional groups exhibit basic
behavior
*Bases- because they contain amine
functional groups
To avoid confusion:
The systems for numbering the atoms in the
pentose and nitrogen-containing base
subunits of a nucleotide are important and
will be used extensively in this lesson. The
convention is that
1. Pentose ring atoms are designated
with primed numbers.
2. Nitrogen-containing base ring
atoms are designated with unprimed
numbers.
Pyrimidine Derivatives
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine ©
- Uracil (U)
Purine Derivatives
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
Adenine, guanine, and cytosine are found in
both DNA and RNA.
Uracil is found only in RNA, and thymine
usually occurs only in DNA