- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
General Biology Notes
Course: Bachelor of Science in Biology (BSBiol)
53 Documents
Students shared 53 documents in this course
University: Saint Louis University (Philippines)
Was this document helpful?

Processes Involved in Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering- DNA modification is the process of adding new traits to an organism through advanced techniques.
DNA recombination- is a process of combining DNA from different sources to create new traits.
Basic steps in Genetic Engineering
Genetic Codes- MRNA (Messenger RNA), AT-CG (Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Cytosine pairs with Guanine), TRNA
(Transfer RNA), AU-CG (While DNA has the ATCG nitrogenous bases, RNA replaces thymine with uracil, making its bases
AUCG. So, that means that whenever DNA has adenine, instead of pairing this with thymine, RNA will use uracil instead).
DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an
organism.
RNA- it is made of nucleotides. Creates proteins via translation.
Protein- repairs cells and makes new ones.
Double Helix- The structure of DNA.
-HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH-
-4.6 billion years ago the Earth started to form.
STRATA- layers on the lithosphere, it has record of life forms and geologic
events in Earth’s History.
FOSSILS- are remnants, Remnant, impression, or trace of an animals or
plants of a past geologic age that has been preserved in Earth’s crust.
The complex of data recorded in fossils worldwide – known as the
fossils record – is the primary source of information about the history
of life on Earth.
-A record of life forms and geologic events in Earths’ history
4.6 BILLION YEARS AGO PRESENT TIME
EON- the largest division of geologic time scale; half billion- nearly
2 billion years.
PRECAMBRIAN- 4.5 billion years; about 88% of Earth’s History
Proterozoic
Archean
Hadean
PALEOZOIC ERA
-ERA- Divisions that span time periods of tens to hundreds of millions
of years
Paleozoic Era
Mesozoic Era
Cenozoic Era
PALEOZOIC ERA
“Ancient or old life”; started more than 540 million years ago.
Many organisms that have emerged during this time were invertebrates.
PERIOD- A division of geologic history with spans of no more than 100 million years
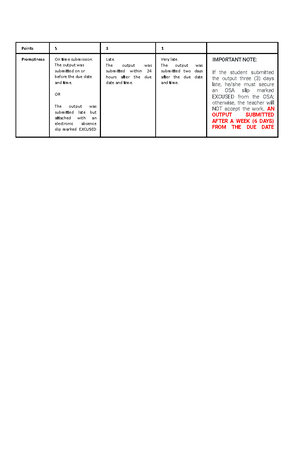
TRANSFORMATION
LIGATION, INSERTION
CUTTING EXPRESSIONISOLATION