- Information
- AI Chat
Eim10q2m1 - eim module
BSE Science
University of Caloocan City
Preview text
NOT
TECHNOLOGY AND
LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation
and Maintenance
Quarter 2 - Module 1
Electrical meter connection and
grounding
Department of Education ● Republic of the Philippines
10
Technology and Livelihood Education Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Grade 10 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 2 - Module 1: Electrical meter connection and grounding First Edition, 2020
Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for the exploitation of such work for a profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalty.
Borrowed materials (i., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this book are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them.
Published by the Department of Education – Division of Bukidnon
Development Team of the Module Writer/s: Uldarico H. Turtosa Jr. Editor/s: Emmanuel T. Yap Reviewer: Mary Jane Ramalloza Cardente PhD Management Team Chairperson: Dr. Arturo B. Bayocot, CESO III Regional Director Co-Chairpersons: Dr. Victor G. De Gracia Jr. CESO V Asst. Regional Director Randolph B. Tortola, PhD, CESO IV Schools Division Superintendent Shambaeh A. Usman, PhD. Asst. Schools Division Superintendent Dala Epra B. Magnaong, PhD. Chief ES, CLMD Neil A. Impogo, PhD. EPS, LRMS Members: Elbert R. Francisco, PhD., Chief ES, CID Mary Jane R. Cardente, PhD., EPS in Technology and Livelihood Education Bienvenido U. Tagolimot Jr., EPS-ADM Rejynne Mary L. Ruiz, PhD., LRMDS Manager Jeny B. Timbal, PDO II Sheila O. Bolasco, Division Librarian II Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education – Division of Bukidnon Office Address:Fortich Street, Sumpong, Malaybalay City
Telephone/Telefax: (088) 813- E-mail Address: bukidnon@deped.gov Website: depedbukidnon.net
Introductory Message
For the facilitator:
Welcome to the Electrical Installation and Maintenance 10 Alternative Delivery Mode
(ADM) Module on, Install Standard Electrical Protection System For Lighting And
Grounding: Electrical meter connection and grounding
This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators from public to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the
standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and
economic constraints in schooling.
This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent
learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help
learners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration their
needs and circumstances.
In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body of
the module:
For the learner and for the Parents;
Welcome to the Electrical Installation and Maintenance 10 Alternative Delivery Mode
(ADM) Module on, Install Standard Electrical Protection System For Lighting And
Grounding.
The hand is one of the most symbolized part of the human body. It is often used to
depict skill, action and purpose. Through our hands we may learn, create and
accomplish. Hence, the hand in this learning resource signifies that you as a learner
is capable and empowered to successfully achieve the relevant competencies and skills at your own pace and time. Your academic success lies in your own hands!
This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for
guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to
process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner.
iii
Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners.
This module has the following parts and corresponding icons:
What I Need to Know
This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module.
What I Know
This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module.
What’s In
This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one.
What’s New
In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation.
What is It
This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills.
What’s More
This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module.
What I Have Learned
This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson.
What I Can Do
This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns.
Assessment
This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency.
iv
####### Table of Contents
Page COVER PAGE COPYRIGHT PAGE TITLE PAGE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lesson 1: Electrical meter connection
What I Need to Know 1 What I Know 1 What’s In 2 What’s New 2 What Is It 3 What’s More 6 What I Have Learned 7 What I Can Do 7 Additional Activities 9
Lesson 2: Electrical grounding
What I Need to Know 10 What I Know 10 What’s In 11 What’s New 11 What Is It 12 What’s More 16 What I Have Learned 17 What I Can Do 17 Additional Activities 19
Post-Test .................................................................................... 20
Key to Answers ....................................................................................... 23
References ....................................................................................... 24
Vi
What I Need to Know
This module was designed and written to help you master the learning competencies in TLE-EIM 10. The scope of this module permits it to be used on different situations.
This module covers the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required in installing a standard electrical protection system for lighting and grounding(EP)
After going through this module, you are expected to perform:
Electrical meter connection and grounding Follow safety procedure
####### vii
II-Identification: Identify the labeled parts, choose your answer from the word box
A. Metering Connection
Meter ground, Ground rod, meter prongs, service lateral, meter base, breaker box, service entrance, breaker, meter
III-Matching Type: Match column A with column B
A B __1. Electricity Flat-rate Meter a. With 3 types known as net meters, bi- directional and generation meter. __2. Electricity Interval Meter b. measure your energy digitally, and can calculate not only the amount of electricity used, but when this energy was consumed, no need for a meter reader to come by your property
__3. Electricity Smart Meter c. more advanced than traditional types records energy use in half-hour intervals. They often have a digital display.
__4. Solar Meter d. Also known as an ‘accumulation meter, these types of meters record your electricity consumption since the meter was first installed
x
What’s In
In your past lessons, you have learned different symbols used in an electrical plan as your bases for installation. As you go on, you must be an insightful viewer for you to have the option to share experiences dependent on the thoughts introduced in the materials you are going to see.
M
A B
- Which symbol is used to represent energy meter in an electrical plan?
- Why do symbols were used instead of real picture in an electrical plan?
Symbol A is an electric motor, therefore Symbol B is basically used in representing energy meter in an electrical plan. Using symbols makes representation simpler and easy to understand.
What’s New
Take a look at the figure below, it shows different energy meter.
A B
Figure 2 waterheatertimer/how to install electric meter Which one is installed in your home? Where does the meter reader look for power consumption?
2
M
What Is It
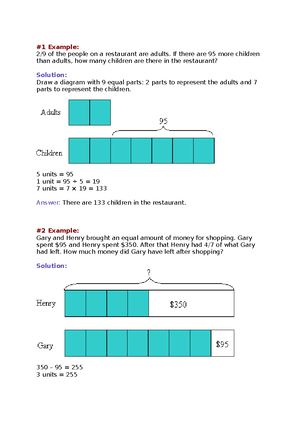
What is an Electricity Meter? An electricity meter, electric meter, electrical meter, or energy meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or electrically powered devices. It measures electricity consumption in kilowatt- hours(kWh). Your billing will be based on the differences between two consecutive readings, by subtracting the most recent with the previous one.
Typically a meter is installed at the point where the power lines enter your building. It consists of prongs plugged into the meter base, a meter number which is registered to a specific consumer, a register which record power consumption, transparent cover that protects mechanism, a seal that serves as authentication to prevent tampering, and a nameplate that bears the manufacturer.
6/13/2020 waterheatertimer/how to install electric meter
4 Types of Electric Meter
Currently, there are four types of electrical meter available in the market. Most of us have a traditional type of reader, known as an accumulation meter or flat-rate meter. Below, you can read more about each meter type, how they work, and what they look like and decide what to install in your household.
Electricity Flat-rate Meter
Also known as an ‘accumulation meter’, these types of meters record your electricity consumption since the meter was first installed. If you have a flat-rate meter, you will need to read your energy usage by checking how much energy your household consumed since last checking it. A technician will need to visit your property to physically check the meter and record the data[2].
waterheatertimer/how to install electric meter
Figure 3
3
Materials and devices used in meter installation
A meter box is a device used to house a building's electrical meter.
youtube/watch?v=_yxOG6GUWVA
Adapter/Locknut -Use to secure rigid and IMC conduit and various threaded fittings to steel outlet boxes and other metal enclosures. Zinc plated for corrosion resistance, these conduit locknuts can be used for outdoor applications.
(RSC or EMT pipe 3/4′′” dia)Conduit, usually fabricated of steel, which encloses electrical wiring, thereby protecting the wiring from outside damage.
Clamps/Straps conduit clamps or pipe clamps allow the pipes to be safely attached to walls or ceilings, so wiring is kept out of harm’s way.
Conduit fittings are connectors and fittings used to connect one piece of conduit to another or to connect conduit to an electrical box.
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit.
7/19/2020 menards/main/electrical/circuit-protection-distribution/
the electrical box has to be attached outside the home, regulation was imposed by the fire department, so they can quickly shut off all the electricity to the house in case of fire.
7/19/2020 menards/main/electrical/circuit-protection-distribution/
Service Entrance wire minimum of 8 size of copper wire, color-coded with the protective ground is green or green with a yellow stripe. The neutral is white, the hot (live or active) single-phase wires are black, and red in the case of a second hot wire.
6/12/2020 thespruce/ 5
Meter Offset - use to connect between metallic conduit and electric meter
6/15/2020 thespruce
Electric Meter box/base installation (pole)
Figure 7 shows how a meter box is installed. The metallic box/base has to be weatherproof if installed outdoors on a metallic pole. The meter box can't be less than 4 feet high or not higher than 6 feet high from floor level. A conduit is connected to the meter box(2) using an adapter/locknut indicated by number 1(service entrance). Insulator of neutral wire with standard color is removed and screwed at the middle of the meter box indicated by number 9(metering ground). Likewise, a breaker box(3) is grounded all the way to ground rod(5). A circuit breaker(6) is installed with an amperage based on the requirement. Another conduit is connected right after the breaker box(4) as service lateral to the main panel. All metallic meter boxes must be grounded. Energy meter(7) installation is actually done by service provider field electricians, simply by plugging-in the specific prongs(8) to the socket of the meter box. Figure 7
What’s More
More on metering installation
Watch a video clip on connecting meter base to the breaker box. youtube/watch?v=_yxOG6GUWVA
6
Self-check
Write your answer in separate sheet of paper
I-Matching Type:Match column A with column B: write in separate sheet
A B
a. Service lateral b. breaker box c. ground rod d. service entrance e. electric meter f. meter base g. prongs h. circuit breaker i. meter ground j. service cap
II-Multiple choice: choose the letter of the correct answer
- Which is the symbol of the standard unit of electricity supplied to the consumer, which is equal to 1 kilowatt acting for 1 hour? a) kWh b) mAh c) Mbp d) Hz
- Meter box may be installed not less _____ in height. A. 4 ft B. 5 ft C. 6 ft D. 7 ft
- Santos family has a record of 09877 for the previous electric bill, and the current billing reads 09897 for the consumption in one month. Which is the total electric consumption of the family? a) 18 kWh b) 19 kWh c) 20 kWh d) 21 kWh
- What does electric meter measures? a) Amount of resistance b) Amount of energy consumption c) Amount of Power d) Amount of Voltage
- How many dial/s are there in an analog electric meter? a) 5 b) 6 c) 7 d) 8
8
Additional Activities
Meter base and breaker box installation Electrical meter boxes can be installed outdoors or indoors. The PEC, or Philippine Electrical Code, specifies that any electrical installation must comply with the residential code of the country where the installation is taking place. All metallic meter boxes must be grounded[12].
Determine the location for the electrical meter box, as well as the height of the box. The metallic box has to be weatherproof if installed outdoors on a metallic pole. The meter box can’t be less than 4 feet high or higher than 6 feet high from floor level. The recommended height of the meter box is 5 feet.
Open a knock out on top of the meter box to fit the riser pole width. Insert the meter box into the riser pipe, then secure it with a connector and a locknut of the same size as the pipe used. There are four screws on each of the box’s corners, which is used in securing the box to the wall or metallic post.
youtube/watch?v=8m5CVTRmxVA 3. Open another knock out at the bottom of the meter box. This will carry the wires going to the service panel or breaker box for outdoor installation. Secure the pipe with a connector and a lock nut that fits the pipe. Now the electrical meter box installation is complete. Cover the box and request inspection from the local utility
company(i. BUSECO). youtube/watch?v=F7HGvRvR-Hs Assessment Criteria WORKMANSHIP 5 pts.
Your score
ACCURACY OF TESTING 4 pts. USE OF TOOLS AND INSTRUMENTS
3 pts.
USE OF PPE 3 pts. SPEED 3 pts. HOUSEKEEPING 2 pts. TOTAL 20 pts.
9
Eim10q2m1 - eim module
Course: BSE Science
University: University of Caloocan City

- More from:BSE ScienceUniversity of Caloocan City350 Documents