- Information
- AI Chat
General Biology Week 1 - Modules SHS
BSE Science
University of Caloocan City
Preview text
GENERAL BIOLOGY I
FIRST QUARTER
Module 1
Let’s CELL-ebrate
Life
####### Most Essential Learning Competency:
####### Explain the postulates of the cell theory;
####### Describe the structure and function of major and
####### subcellular organelles (STEM_BIO11/12-Ia-c-2)
12
As we aim to make distance learning seamless and effective, here are some rules and tips to maximize learning and productivity in a new normal setup.
- Establish a routine. Set up a timetable to plan and schedule your task.
- Find a comfortable workspace. Choose a specific place in your house that is free from distractions, this will keep you focused and increases productivity.
- Get yourself prepared. Prior to starting your modules, make sure everything is ready and organized. Follow carefully all the contents and instructions indicated in every page of this module.
- Self – care. Avoid feeling tired. Get up occasionally to take short breaks to either grab a snack or close your eyes while taking deep breaths. Keep your mindset in check.
- Ask questions. If there are items in the module that you cannot understand, do not hesitate to post your queries.
- Reflect and practice. Analyze posttests and create a personal conclusion of the lesson.
In this module, you will establish understanding of cell theory, cell structure and functions. Specifically, this module helps you to: enumerate and explain the postulates of the cell theory (STEM_BIO11/12-Ia-c-1); describe the structure and function of major and subcellular organelles (STEM_BIO11/12-Ia-c-2).
Directions: Read the questions carefully. Write the letter of the correct answer on the blank provided before the number.
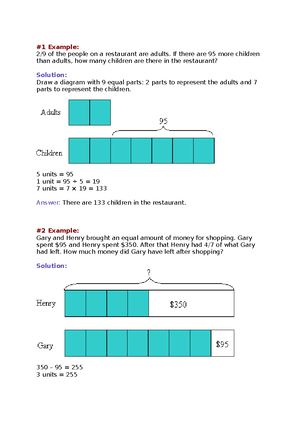
____1. Structures in the living world are organized in hierarchical levels. The cellular level serves to be the lowest. What level is next to cellular level? A. cell C. organ B. tissue D. system ____2. Which instrument is essential in the development of cell theory? A. spectrogram C. telescopes B. caliper D. microscopes ____3. Who was the first scientist to see cells under the microscope, and coined the term CELL? A. Theodor Schwann C. Robert Hooke B. Matthias Schleiden D. Anton van Leeuwenhoek ____4. What structure serves as the outer boundary of the cell? A. cytoplasm C. cell membrane B. nucleus D. flagella ____5. Which of the following is NOT a component of cell theory? A. All living things are composed of one or more cells. B. Cell is the basic unit of life. C. All cells are membrane bound. D. All cells came from pre-existing cells.
To the Learners
Expectations
Pre-Test
UNVEILING HISTORY
Objective: Enumerate and explain the postulates of cell theory. Procedure: Study the timeline and analyze the conceptualization of cell theory.
Guide Question: 1. From the timeline presented, what three statements best describe cell theory? Explain each postulate. 2. How did the invention of microscope contribute to the discovery of cells? 3. If the above scientists did not pursue their works and shared their contributions to the world, do you think the idea that “all organisms are made up of cells”, would exist? Justify your answer.
1600
1665 Robert Hooke published his book Micrographia, which contains his drawings of a section of cork, as seen through one of the first microscopes.
1683 Leeuwenhoek discovered bacteria.
1700
1900
####### 1674
Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed tiny living organisms in drops of pond water through his simple microscopes.
1839 Theodor Schwann concluded that all animals are made up of cells.
1838 Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants are made up of cells.
1855 Rudolf Virchow proposed that all cells come from existing cells, completing the cell theory.
Cell Theory Timeline
Activity 1
Objective: Describe and identify the functions of the basic structures of the cell.
Cells differ in size and shape; most of them have basic structures. The cell
structure comprises individual components with specific functions essential to carry out life's
processes. The cells of animals, plants, and related organisms have three basic structures:
- Cell Membrane – is the outer boundary
of the cell. Phospholipid bilayer; Semi- permeable, that it controls what goes in and out of the cell.
- Nucleus – houses DNA and directs
synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.
- Cytoplasm - provides structure to the
cell, site of many metabolic reactions; medium which organelles are found.
Quick Lab:
Procedure: Make a model of cytoplasm.
- Fill a jar/wide-mouthed bottle with water.
- Add unflavored gulaman and stir.
- Shine a light through the jar/bottle for 3 minutes.
Guide Questions: 1. Describe what you have observed upon flashing the light to the jar/bottle. 2. How would you compare the gulaman to the cytoplasm? 3. What do you think would happen if there is no existing cytoplasm inside the cell?
Activity 2
Cell membrane
cytoplasm nucleus
Figure 1. Basic structure of a cell
As stated in the postulates of cell theory, both plants and animals are made up of cells. Each of them has organelles that carry out cellular processes. The organelles of a plant cell and their functions are almost similar to those found in animal cells (refer to activity 1). Thus, there are only few organelles that can be exclusively seen in a plant cell for they have specialized functions.
Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy. Most of the living world runs on the energy provided by photosynthesis, which is the conversion of light energy from the sun to the chemical energy of sugar molecules. It is also enclosed by an inner and outer membrane separated by a thin intermembrane space. The compartment interior the inmost membrane holds a tenacious fluid called stroma, which carries chloroplast DNA and ribosomes. Thylakoids are network of interconnected sacs inside the chloroplast and these are stacked like poker chips; each stack is called granum. It is known to be the solar power sac of the chloroplast. The site where the green chlorophyll traps solar energy.
####### ORGANELLE FUNCTION/S
Cell Wall
Located outside the cellmembrane and is primarily made ofcellulose Maintains the shape and protects the plant cell
Chloroplast
Substances inside the chloroplast help a green plant cell trap the sun’s energy and then produce food chlorophyll, which is the green pigment responsible forcapturing light during photosynthesis The lumen is the spaceinside the thylakoid Central Vacuole Maintains the turgorpressure to keep theplant cell from wilting
Plasmodesmata
Traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them Peroxisome
sugar and assistingConverts fatty acids to chloroplasts in photorespiration
Figure 3. Parts of a Plant Cell
Remember
Figure 4. Parts of Chloroplast
commons.wikimedia/wiki/File:Features_of_a_chloroplast
PICTURE ANALYSIS
Directions: Write your answers on a separate paper to be attached in this module. 1. Describe the condition of the plant? 2. What is the role of the environment in the state of the plant? 3. Correlate the function of the central vacuole in maintaining the healthy state of a plant. 4. When the turgor pressure decreases, what happens to the plant? Explain your answer. 5. Analyze what will happen to the plant if the central vacuole will lose too much water? 6. What general function do chloroplast and mitochondrion have in common?
Directions: Read the questions carefully. Write the letter of the correct answer on the blank provided before the number.
____1. Which characteristic of the cell membrane is described as the capacity to regulate what goes in and out of the cell? A. high permeability C. permeability B. selective permeability D. none permeability ____2. Which of the following statements is always TRUE? A. All cells have cell wall. C. All cells contain a chloroplast. B. All cells contain nucleus. D. All cells have cell membrane. ____3. Cell membranes are constructed mainly of _________________________. A. lipid bilayer C. calcium ions B. protein pump D. carbohydrate gates ____4. How do cells arise from pre-existing cells? A. through reproduction C. through metabolism B. through adaptation D. through growth and reproduction ____5. Which of the following is NOT a component of cell theory? A. All living things are composed of one or more cells. B. Cell is the basic unit of life. C. All cells are membrane bound.
####### D. All cells came from pre-existing cells. 7
Post-Test
Check Your Understanding
General Biology Week 1 - Modules SHS
Course: BSE Science
University: University of Caloocan City

- More from:BSE ScienceUniversity of Caloocan City350 Documents