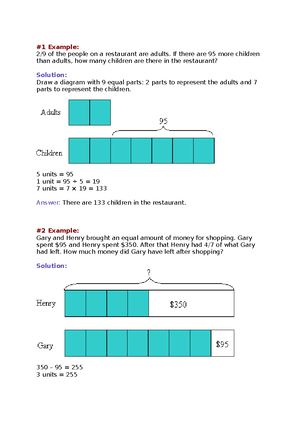
- Information
- AI Chat
General Biology Week 3 - MODULES SHS
BSE Science
University of Caloocan City
Preview text
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL
FIRST QUARTER
Module 3
THE CELL CYCLE
Prepared by: SUZZETH U. DIZON, MBio Master Teacher I – Caloocan City Science High School
Most Essential Learning Competency:
Characterize the phases of the cell cycle and their control
points (STEM_BIO11/12-Id-f-6)
Describe the stages of mitosis/meiosis given 2n=
(STEM_BIO11/12-Id-f-7)
12
TO THE LEARNERS:
This module is intended for STEM Senior High School Student taking General Biology I as their specialized subject. As learners, you must execute the activities in this module and must be submitted to the teacher on a specified date. It will be an advantage if you will read something about the topic and use some learning modalities provided by the teacher to ensure there is gain of knowledge in this topic.
This enables you to appreciate the importance of knowing the events happening in our body at the cellular level, connect your previous learnings about the biological organization of life (from cell to tissue to organ to body system to individual), and relate the topic to practical events in your life.
The module has activities and tests that you are required to answer. These should be done to help you deepen your understanding of the concepts. Remove any unnecessary things around you in order for you to concentrate and focus on answering the module.
EXPECTATIONS:
The module is all about THE CELL CYCLE which is covered by the following Most Essential Learning Competencies in General Biology I:
- Characterize the phases of the cell cycle and their control points (STEM_BIO11/12-Id-f-6);
- Describe the stages of mitosis/meiosis using 2n=6 (STEM_BIO11/12-Id-f-6)
In here, the following objectives are expected to be attained by the learners:
- characterize the cell cycle checkpoints using pie chart;
- characterize the different phases of cell division (using a video presentation if available);
- describe the different stages of mitosis/meiosis (using video presentation if available); and
- determine the stages of mitosis using a prepared slide of onion root tip.
The teachers are expected to provide resources and references for the said topic which can be provided to learners, it could be a reading text, diagrams, online links, or video demonstrations. The teacher may also discuss using an online platform or through a recorded video.
LOOKING BACK
You have encountered from the previous lesson about the basic parts of the cell as well as how cells are involved in the biological organization of life. Answer the activity below to recall your knowledge about it.
WORD GAME: Identify the cell organelle/structure using the description given and the number of letters corresponded by the boxes.
It is the control center of the eukaryotic cells that regulates its activities and contains the genetic material of the individual.
The material inside the cell enclosed by the cell membrane.
The threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
It is a mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division.
It is the double membrane that encloses the nucleus.
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
All living organisms follow a specific life cycle, animal life cycle and the alternation of generation. Eukaryotic cells also has its own life cycle and we call it as the CELL CYCLE. Cell cycle is a repeating sequence of cellular growth and division. It is made up of different phases, each has its own unique process or event (refer to Figure 2).
In order to ensure the cell cycle regulation, critical points called ‘checkpoints’ must also be identified. Figure 3 below shows the location of these checkpoints in the cell cycle.
Ninety percent of the whole cycle is covered by Interphase which includes the G1, S, and G2 stages while the remaining 10% is for the M phase, or the nuclear division proper of the eukaryotic cell. ‘M’ could be mitosis (somatic cells) or meiosis (gametes). Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells. Focusing on the cell division of somatic cells, mitosis is divided in to four phases namely: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase; which is the followed by the division of the cytoplasm known as ‘cytokinesis.’
Figure 2 Cell Cycle and its events www2.le.ac/projects/vgec/highereducation/ topics/cellcycle-mitosis-meiosis
Figure 3 Cell Cycle and its checkpoints courses.lumenlearning/wmopen-biology1/chapter/cell- cycle-checkpoints/
ACTIVITY NO. 1: THE CELL CYCLE and CHECKPOINTS
Activity 1 Direction: Describe each event of the cell cycle by completing the information below (give at least two).
Event Description of events G1 phase 1. 2. S phase 1. 2. G2 phase 1. 2. G0 phase 1. 2. M phase 1. 2.
Activity 1 Direction : Give the function of the following checkpoints:
G1 checkpoint G2 checkpoint M checkpoint
You may read the article at khanacademy/science/biology/cellular-molecular- biology/mitosis/a/cell-cycle-phases no access, please ask your teacher to provide a hard copy for you.
Online Option: (This is an optional activity. If you have access to the internet you may accomplish this one to further assess your understanding about the cell cycle.)Access highered.mheducation/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter10/how_the_cell_cycle_works. html and answer the online quiz. Screenshot and paste your answers and your score below.
ACTIVITY NO. 2: M PHASE
Activity 2 Instruction:
Yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) is known to be a vector for several viruses like Dengue virus, Chikungunya virus and Zika virus. Just like any other common insects with few number of chromosomes, A. aegypti has 2n=6 genetic information.
Make a graphic organizer to show how mitosis and meiosis is happening on this insect.
MITOSIS MEIOSIS
You may use a separate sheet of paper for this activity. (Note: digitally or manually made outputs are acceptable)
Question: What is/are the difference/s of mitosis and meiosis?
Online Option: (This is an optional activity. If you have access to the internet you may accomplish this one to further assess your understanding about the mitosis and meiosis.)
Figure 6 Aedes aegypti, also known as the yellow fever mosquito with 2n=6 genetic make up. en.wikipedia/wiki/List_of_organisms_by_chromosome_count#/media/File:Aedes_aegypti
REMEMBER
- Cell cycle is the repeating sequence of cellular growth and division of eukaryotic cells. It is divided into 2 major phases: Interphase and M phase. Interphase is the longest phase which is divided into three sub phases: G1, S, and G2 phases, each has its own unique structural and metabolic events.
- M phase is the nuclear division itself. It could be mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is the nuclear division of the somatic cells, producing diploid cells from a diploid parent. It is divided into four stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, ad Telophase (PMAT). As the nuclear division is about to end, cytoplasmic division simultaneously occurs which is known as ‘cytokinesis’ and is characterized by the formation of cleavage furrow in animal cells and cell plate in plants. Therefore, a diploid parent cell produces a genetically identical two daughter cells.
- Meiosis is type of cell division that is involved in the formation of gametes. It is divided into two phases: Meiosis I which is known as the reduction phase as the diploid cell becomes haploid; and Meiosis II which is known as the replication phase with process similar to mitosis. Thus, a diploid parent cell can produce four haploid daughter cells.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
Direction: Write TRUE if the statement is true, otherwise write FALSE.
1. All cells enter G0 phase.
2. Cytokinesis happens after anaphase.
3. Plants also undergo cell cycle and meiosis.
4. Mitosis is involved in tissue and body repair.
5. The parent cell in meiosis is a haploid cell.
6. In 2n=6 genetic make-up, 6 is the haploid chromosomes.
7. Meiosis produces sex cells that are diploid in number of chromosomes.
8. G1 checkpoint checks on the cell size and DNA damage.
9. In gamete formation, there is only one interphase in the whole cell cycle.
10. During metaphase, cell becomes larger as the chromosomes move to the opposite ends.
POST TEST
Directions: Read the questions carefully. Write the letter of the correct answer.
- Which is the correct sequence of events in the cell cycle?
A. DNA synthesis Increase in size Duplication of organelles B. Increase in size DNA synthesis Duplication of organelles C. Increase in size Duplication of organelles DNA synthesis D. Duplication of organelles DNA synthesis Increase in size 2. Which is NOT a cell cycle checkpoint? A. G0 checkpoint C. G1 checkpoint B. G2 checkpoint D. M checkpoint 3. Which statement is true about meiosis? A. It is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells identical to the parents. B. It is commonly happening on somatic cells involving tissue repair. C. It produces two haploid daughter cells. D. It is involved in gamete formation. 4. Which stage of mitosis is shown in the figure below?
flickr/photos/carolinabio/6141866930/in/photostream/ A. Prophase C. Anapase B. Telophase D. Metaphase
- Which statement is true? A. All cells enter the G0 phase. B. All cells in the G0 phase will eventually die. C. G0 phase is also the programmed cell death. D. Cancer cells have defective checkpoints and programmed cell death.
General Biology Week 3 - MODULES SHS
Course: BSE Science
University: University of Caloocan City

- More from:BSE ScienceUniversity of Caloocan City350 Documents