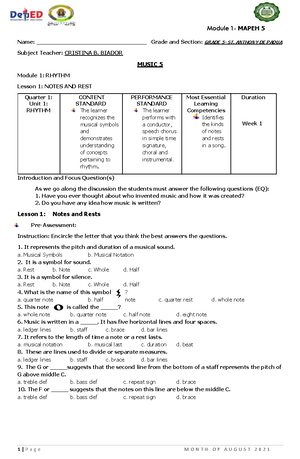
- Information
- AI Chat
(f) Reviewer- Quizf - C NCXN
C NCXN
Course
Rhythmic Activities (PE002)
31 Documents
Students shared 31 documents in this course
University
University of Caloocan City
Academic year: 2023/2024
Uploaded by:
Anonymous Student
This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous.
University of Caloocan CityStudents also viewed
Related documents
- F2f pe m1 - Lecture materials with activities
- Tagalog-numbers - Angela
- Tungcab PE003 Module 7 Unit 3 Badminton Fundamental Skills
- Activity 1 (PE) performance task
- Action Reseach in Teacher Education Example
- PE 111-Module 1-Unit 1-Introduction-to-Physical-Education-and Fitness-Definition of the Physical Education and Objectives of Physical Education
Preview text
MODULE 1: CATERING
Catering is the prearranged service of food and drinks to clients for different occasions. This
module focuses on the types and classification of catering services by distinguishing on-premise
and off-premise catering. It presents catering events that fall under each category and define
the three catering segments:
(1) Commercial;
(2) Non-commercial; and
(3) Military, and the activities for each segment.
LESSON 1 Types of Catering Services
1. Identify and describe the attributes of the two main types of catering; and
------------------------------------------------------------------------
On-premise Catering- The caterer has his own dining hall with an attached kitchen
or production area.
Types of catering events which may occur in on-premise catering:
1. Hospital Catering: Events that occur within a hospital environment;
2. High School/Elementary School Catering: Events that may occur anywhere in the
school property but food preparation is done in the school cafeteria; and
3. University/College Catering: Provides food and related services to students,
faculty, administrators and guests.
Off-premise Catering. The caterer brings the complete service to the customer.
This may be at a private home, church, office, school or any type of outdoor affair.
He is provided with a kitchen. He brings his own facilities and equipment for food
production, transport and service.
Types of off-premise catering:
1. Supermarket Catering: Provide items that can be picked up and taken home or to
another location;
2. Dual Restaurant-Catering Operations: When a restaurant operator evolves into
catering services to strategically increase the efficiencies of the base operation;
3. Conventions and Weddings Catering: Provides food service to support
professional, business and social activities of a large group of people.; and
4. Mobile Catering: Employs one or a fleet of trucks to support an assortment of
food and beverages for customers located at diverse locations.
On-premise and Off-premise Combinations. Hotels and small restaurants may
prepare food in their kitchen and transport off-premise to another location to serve their
guests.
LESSON 2 Classification of Catering Services
1. Differentiate the catering segments;
2. Provide activities for each segment; and
3. Enumerate the requirements for selection of caterer.
II. Content
Classification of Catering Segments
1. Commercial Segment: For-profit operations; financial goals include a profit gained
from revenue minus expenses.
- Independent caterers
- Hotel/motel caterers
- Home-based caterers
- Restaurant/Catering firms
- Private clubs
2. Non-commercial Segment: Not-for-profit operations; operates on a break-even basis
where revenue equals expenses. Catering services are provided as a complimentary
service.
- ·Business/Industry accounts
- College/University catering
- Health care facilities
- Recreational food service
- School catering
- Social organizations
- Transportation foodservices catering
3. Military Segment: For military or diplomatic events; operates on a break-even basis.
- Military functions
- Diplomatic functions
LESSON 3 Selecting a Caterer
1. explain the symbiotic relationship of the seven functions of catering;
2. explain how to formulate a catering plan;
3. describe why a menu is one of the important elements of a catering plan;
4. define sanitation and explain its importance in a dining room capacity;
LESSON 1: The Seven Functions of Catering
The Seven Functions of Catering
1. Planning -the process of detailing and outlining all tasks required to accomplish the
objective. The plan helps the caterer identify objectives derived from the mission
statement. The plan is a blueprint that leads everyone toward a common goal.
2. Operations. Execution of Tasks - the process of listing the tasks and steps for executing
the plan. It also includes assigning tasks to employees for execution.
3. Organizing the event-the process of forming the organization so each assigned task
can achieve the stated objective.
4. Equipment - these are based on the menu, service requirements, type and location of
event, and special needs of the client.
5. Implementing - the process of using effective communication skills to put the plan
into action
6. Controlling- ensures the effective and efficient use of the caterer's resources in
providing service to accomplish goals.
7. Understanding insurance and legal issues - ensures the basics are covered to
protect one's livelihood. This includes creation of team to do routine safety checks of the
staff, equipment and procedures to ensure proper compliance with HACCP standards.
HACCP- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point
- is a management system in which food safety is addressed through the
analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical
Tools and Equipment
IN CATERING BUSINESS
Obtaining Equipment
Off-Premise Safety
Storage For Equipment
OBTAINING EQUIPMENT
Catering Equipments
Holding Cabinets
Chafing Dishes
Food Pan Carriers
Hot Food Tables and Accessories
Catering Cart
Catering Supplies
Catering Service Trays
Ice Beverage Bins
Insulated Beverage carrier
Punch Bowls
Tabletop and Buffet Display
Food and Drink Fountains
Ice Sculpture Molds
OFF-PREMISE SAFETY
Written Food Safety Management System
Washing Facilities
Water Containers
Refuse
Food Handling Practices
Personal Hygiene
First Aid
STORAGE FOR EQUIPMENT
Catering Supplies that can be stored in a Storage Unit
Extra Tables & Chairs
Decoration or Linens
Inventory
The choice of furniture and its layout and the linen, tableware, small equipment and
glassware will be determined by factors such as:
the type of clientele expected
the site or location of the establishment
the layout of the food and beverage service area
the type of service offered
the funds available.
The general points to be considered when purchasing equipment for a food and
beverage service area are:
The flexibility of use
type of service being offered
type of customer
design
colour
durability
ease of maintenance
stackability
cost and funds available
availability in the future – replacements
storage
rate of breakage, i. crockery
shape
psychological effect on customers
delivery time.
Front-of-house service areas are some of the busiest of a foodservice
establishment, especially during the service periods.
The service areas behind the scenes are known as back-of-house areas. These
areas include the stillroom, hotplate (or pass) area and the wash-up. These
areas include the stillroom, hotplate (or pass) area and the wash-up.
The back-of-house service areas are usually between the kitchen and food and
beverage service or front-of-house areas.
The back-of-house areas must also be efficiently organised, stocked with well-
designed equipment and appropriately supervised.
3 Stillroom - stillroom provides items of food and beverages required for the
service of a meal that are not catered for by the other major departments in a
foodservice operation, such as the kitchen, larder and pastry.
Staffing- In a large establishment a stillroom supervisor is in charge of the
stillroom
Equipment- The equipment found in a stillroom is fairly standard and there
tends to be a considerable amount needed because of the wide range of food
items offered and the need to ensure their proper storage, preparation and
presentation.
Provisions
As a basic guide, the following food items would normally be dispensed from
the stillroom.
All beverages such as coffee, tea, chocolate, tisanes, Bovril, Horlicks, Ovaltine
and other drinks.
Assorted fruit juices: orange, tomato, pineapple and grapefruit.
Milk, cream and alternatives.
Sugars: loose, pre-wrapped portions, brown coffee crystals, Demerara,
etc., and alternatives.
Preserves: marmalade, cherry, plum, raspberry, strawberry, apricot and
honey.
Butter:
Sliced and buttered brown, white and malt bread.
Rolls, brioche and croissants.
Bread substitute items: gluten free, rye, rice crackers, etc.
Dry crackers
Assorted breakfast cereals
Toasted scones and teacakes.
Pastries, gâteaux and sandwiches.
- The aboyeur, or barker, is in charge, and controls the hotplate (or
pass) during the service period.
Examples of traditional kitchen terms are:
Le service va commencer: general warning to kitchen that service is about to
commence.
Ça marche trois couverts: indication to the kitchen of the number of covers
on the table, in this case three covers.
Poissonnier, faites marcher trois soles Véronique: example of fish section
informed of the order required, in this case three sole Véronique.
Poissonnier, envoyez les trois soles Véronique: when the order is required at
the hotplate by the waiter, the aboyeur calls it up. In this example it is the fish
section being told to bring the order for the three sole
Véronique.- the reply given by the chef de partie (section chef) to the order
called out by the aboyeur.
the term called out by the aboyeur before the actual order when an extra special
order is required.
Dépêchez-vous: the words used to hurry up an order.
Arrêtez: the term used to cancel an order.
Foods requiring special degrees of cooking are given the following terms:
Omelette baveuse: soft inside. l Steak grillé:
– bleu: (rare) surfaces well browned, inside raw
– saignant: underdone
– à point: medium
– bien cuit: cooked right through, well done.
3 Wash-up
- The wash-up must be sited so that staff can work speedily and efficiently
when passing from the food service areas to the kitchens.
Dishwashing methods
Manual- Soiled ware washed by hand or brush machine
Automatic conveyor- Soiled ware loaded in baskets, mounted on a
conveyor by operators for automatic transportation through a
dishwashing machine
Flight conveyor- Soiled ware loaded within pegs mounted on a
conveyor, by operators for automatic transportation through a
dishwashing machine
Deferred wash- Soiled ware collected together, stripped, sorted and
stacked by operators for transportation through a dishwashing
machine at a later stage
3 Colour and lighting considerations
- The colour scheme used in the foodservice area should help to reflect the
character of the operation.
Lighting- A well-designed colour scheme can easily be spoilt by a badly
planned lighting system and therefore the two aspects should be considered
together at the design stage.
3 Bar
- A major factor is the siting of the bar. The position should ensure the
bar achieves the greatest possible number of sales.
Area
- The bar staff must be given sufficient area or space in which to work
and move about. There should be a minimum of 1 m (3 ft 3 in) from
the back of the bar counter to the storage shelves and display cabinets
at the rear of the bar.
Layout
- During initial planning, careful consideration must be given to the
layout of the bar. Adequate storage for the stock and equipment listed
above must be provided in the form of shelves, cupboards and racks.
Everything should be easily to hand so that bar staff do not have to
move about more than necessary to provide a quick and efficient
service.
Plumbing and power
- It is essential to have hot and cold running water for glass washing.
Power is necessary for the cooling trays, refrigerators and ice making
machines.
Safety and hygiene
- Great care must be observed to ensure that the materials used in the
make-up of the bar are hygienic and safe.
3 Furniture
- Furniture must be chosen according to the needs of the
establishment
TYPE OF FURNITURE
Loose random Freestanding furniture positioned in no discernible
pattern within a given service area
Loose module Freestanding furniture positioned within a given
service area to a pre-determined pattern, with or without the use of
dividers to create smaller areas within the main area
Booth Fixed seating (banquette), usually high backed, used to
create secluded seating
High density Furniture with minimum dimensions and usually fixed,
positioned within a given service area to create maximum seating
capacity
Module Seating- incorporates tables and chairs constructed as one
and may be fixed to the floor
In situ- Customers served in areas not designed for service, e.
aircraft and hospital beds
Bar and lounge areas- Customers served in areas not primarily
designed for food and beverage service
3 Linen
- There are many qualities of linen in present day use, from the finest Irish linen and
cotton to synthetic materials such as nylon and viscose
- should be used only for its intended purpose in the restaurant and not for cleaning
purposes,
TableCloths- square or a round table1 m (3 ft) in diameter
Slip cloths- l 1 m x 1 m (3 ft x 3 ft) used to cover a slightly soiled tablecloth.
Napkins (serviettes)- 46–50 cm (18–20 in) square if linen, 36–42 cm (14–
in) square if paper.
Buffet cloths- this is the minimum size; longer cloths will be used for longer
table
Storage
Crockery should be stored on shelves in piles of approximately two dozen.
Silver cleaning methods
Silver dip Items to be cleaned are completely immersed in dip in a plastic bowl
for a very short time, rinsed in clean water and polished with a tea cloth. This is
a very quick method but is hard on metal if left in dip too long
Burnishing machine- Items to be cleaned are placed in a drum containing ball
bearings, soap powder and water. The drum rotates and the tarnish is rubbed
off. All items are rinsed in hot water and dried with a tea cloth
Polvit- Items to be cleaned are placed in an enamel or galvanised iron bowl
within which is the Polvit aluminium metal sheet containing holes, together
with some soda.
Plate powder- Pink powder is mixed with a little methylated spirit to a smooth
paste.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel is finished by different degrees of polishing:
high polish finish
dull polish finish
light grey matt, non-reflective finish
EQUIPMENT
1 Asparagus holder Used to hold asparagus spears when eating
2 Sugar tongs Required for cube sugar
3 Pastry slice Sweet trolley – serving portions of gâteau
4 Oyster fork Shellfish cocktail/oysters
5 Pastry fork Afternoon tea
6 Corn-on-the-cob holders One to pierce each end of the cob
7 Lobster pick To extract the flesh from the claw
8 Fish knife To break the fish and push it onto the fork
9 Sauce ladle Service from sauce boat
10 Fruit knife and fork Dessert – cover
11 Nutcrackers Dessert – fruit basket
12 Grape scissors To cut and hold a portion of grapes
13 Grapefruit spoon Grapefruit halves
14 Ice cream spoon For all ice cream dishes served in coupes
15 Sundae spoon Ice cream sweet in a tall glass
16 Snail tongs Used to hold the snail shell
17 Snail dish Dish is round with two ears, having six indentations to hold a
portion (6) of snails
18 Snail fork Used to extract the snail from its shell
19 Cheese knife Cheese board
20 Stilton scoop Service of Stilton cheese
21 Butter knife To serve a butter portion
22 Gourmet spoon Sauce spoon for cover
23 Preserve spoon Used with preserve/jam dish
3 Glassware
The main varieties of disposables are generally used as follows:
storage and cooking purposes
service of food and beverages
décor
hygiene
clothing
packaging
Advantages of disposables
Equipment and labour: disposables reduce the need for washing-up
equipment, staff and materials.
Hygiene: usage improves the standard of hygiene in an establishment.
Time: disposables may speed up service, for example, for fast food.
Properties: disposables have good heat retention and insulation properties.
Marketing: disposables can be used as a promotional aid.
Capital: usage reduces the amount of capital investment.
Carriage: they are easily transported.
Cost: disposables may be cheaper than hiring conventional equipment.
Disadvantages of disposables
Acceptability: customer acceptability may be poor.
Cost: disposables can be more expensive than some conventional
equipment: back-up quantities are required.
Supply: there is heavy reliance on supply and delivery time.
Environment: unless they are made from renewable resources and are
completely biodegradable they have a negative impact on the environment.
3 Automatic vending
It is a form of automatic retailing using one of the following methods of
payment:
coin
banknote
money card
token
free vend.
Types of foodservice vending machine
Merchandiser: customer can view the products on sale, for example, confectionery machines.
Can be used for refrigerated drinks (bottles and cans) and pre-packaged meals and snacks. Can
also be used for hot meals and snacks through internal heating.
Hot beverage vendor: mixes the powdered ingredients with hot water to produce the product.
In-cup system: ingredients are already in individual cups to which hot water is added. l Cold
beverage vendor: by use of post-mix syrup and water (carbonated or non-carbonated).
Micro-vend system: provides a range of hot or cold foods from which the customer may make a
selection and heat in an accompanying microwave oven
(5)The Menu
Originally the bill of fare (English) or menu (French) was not presented anything
from 10 to 40 in number. The first set of dishes were placed on the table before the
diners entered – hence the word ‘entrée’ – and, when consumed, these dishes were
removed or relieved by another set of dishes – hence the words ‘relevés’ or ‘removes’.
This style of service was referred to as service à la française.
The word ‘menu’ dates back to the eighteenth century, although the custom of
making a list of the courses for a meal is much older. Modern menus first appeared
during the early nineteenth century, in the Parisian restaurants of the Palais-Royal. At
this time, France, and later other countries, adopted the style of service referred to as
service à la russe. In this system of service one course is served after another
throughout the meal.
The menu is primarily a selling aid. The design of the menu should be appealing and
interesting to the customer so it encourages them to view its contents
Design considerations of the menu include:
size and shape
Was this document helpful?
(f) Reviewer- Quizf - C NCXN
Course: Rhythmic Activities (PE002)
31 Documents
Students shared 31 documents in this course
University: University of Caloocan City
Was this document helpful?

MODULE 1: CATERING
Catering is the prearranged service of food and drinks to clients for different occasions. This
module focuses on the types and classification of catering services by distinguishing on-premise
and off-premise catering. It presents catering events that fall under each category and define
the three catering segments:
(1) Commercial;
(2) Non-commercial; and
(3) Military, and the activities for each segment.
LESSON 1 Types of Catering Services
1. Identify and describe the attributes of the two main types of catering; and
------------------------------------------------------------------------
On-premise Catering- The caterer has his own dining hall with an attached kitchen
or production area.
Types of catering events which may occur in on-premise catering:
1. Hospital Catering: Events that occur within a hospital environment;
2. High School/Elementary School Catering: Events that may occur anywhere in the
school property but food preparation is done in the school cafeteria; and
3. University/College Catering: Provides food and related services to students,
faculty, administrators and guests.
Off-premise Catering. The caterer brings the complete service to the customer.
This may be at a private home, church, office, school or any type of outdoor affair.
He is provided with a kitchen. He brings his own facilities and equipment for food
production, transport and service.
Types of off-premise catering:
1. Supermarket Catering: Provide items that can be picked up and taken home or to
another location;
2. Dual Restaurant-Catering Operations: When a restaurant operator evolves into
catering services to strategically increase the efficiencies of the base operation;
3. Conventions and Weddings Catering: Provides food service to support
professional, business and social activities of a large group of people.; and
4. Mobile Catering: Employs one or a fleet of trucks to support an assortment of
food and beverages for customers located at diverse locations.
Too long to read on your phone? Save to read later on your computer
Discover more from:
- Discover more from:
Recommended for you
Students also viewed
Related documents
- F2f pe m1 - Lecture materials with activities
- Tagalog-numbers - Angela
- Tungcab PE003 Module 7 Unit 3 Badminton Fundamental Skills
- Activity 1 (PE) performance task
- Action Reseach in Teacher Education Example
- PE 111-Module 1-Unit 1-Introduction-to-Physical-Education-and Fitness-Definition of the Physical Education and Objectives of Physical Education