- Information
- AI Chat
MCQ on Data mining
MCQ on Data mining
Course
Data Mining
91 Documents
Students shared 91 documents in this course
University
Assiut University
Academic year: 2021/2022
Listed bookData Mining: Concepts and Techniques
Uploaded by:
28Uploads
41upvotes
Preview text
Data mining questions bank with answer
1. What is the median of the following set of scores?
18, 6, 12, 10, 14?
a. 10
b. 14
c. 18
d. 12
2. what percentage of scores fall Approximately within one standard deviation of the mean in a
normal distribution?
a. 34%
b. 95% -→ Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean
c. 99% -→ of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
d. 68% ---→ within one standard deviation of the mean
3. ___________ is the goal to focus on summarizing and explaining a specific set of data.
a. Inferential statistics
b. Descriptive statistics
c. None of the above
d. All of the above
4. most frequently occurring number in a set of values is called the ____.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
5. the _______ is the best measure As a general rule of central tendency because it is more precise.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
6. Focusing on describing or explaining data versus going beyond immediate data and making inferences is the
difference between _______.
a. Central tendency and common tendency
b. Mutually exclusive and mutually exhaustive properties
c. Descriptive and inferential
d. Positive skew and negative skew
7. ___________ are used when you want to visually examine the relationship between two quantitative
variables.
a. Bar graphs
b. Pie graphs
c. Line graphs
d. Scatterplots
8. _______ is often the preferred measure of central tendency if the data are severely skewed.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
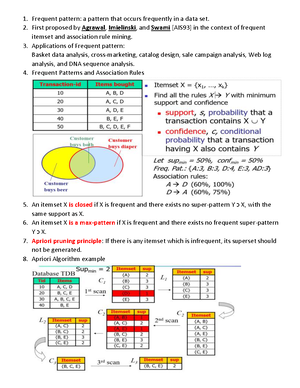
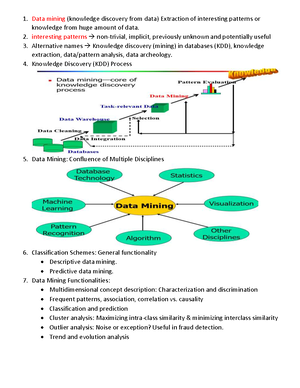
9. ................... is an essential process where intelligent methods are applied to extract data patterns.
A) Data warehousing
B) Data mining
C) Text mining
D) Data selection
10. Data mining can also applied to other forms such as ................
i) Data streams
ii) Sequence data
iii) Networked data
iv) Text data
v) Spatial data
A) i, ii, iii and v only
B) ii, iii, iv and v only
C) i, iii, iv and v only
D) All i, ii, iii, iv and v
11. Which of the following is not a data mining functionality?
A) Characterization and Discrimination
B) Classification and regression
C) Selection and interpretation
D) Clustering and Analysis
A)
12. Hypothesis testing and estimation are both types of descryptive statistics.
a. True
b. False
13. A set of data organized in a participants(rows)-by-variables(columns) format is known as a “data set.”
a. True
b. False
22. which of the following is not involve in data mining?
A. Knowledge extraction
B. Data archaeology
C. Data exploration
D. Data transformation
23. Patterns that can be discovered from a given database are which type...
a) More than one type
b) Multiple type always
c) One type only
d) No specific type
Answer - Click Here:
24. Which of the following is true for Classification?
a) A subdivision of a set
b) A measure of the accuracy
c) The task of assigning a classification
d) All of these
Answer - Click Here:
25. Data mining is?
a) time variant non-volatile collection of data
b) The actual discovery phase of a knowledge
c) The stage of selecting the right data
d) None of these
26. ——- is not a data mining functionality?
A) Clustering and Analysis
B) Selection and interpretation
C) Classification and regression
D) Characterization and Discrimination
27. Which of the following is general characteristics or features of a target class of data?
a) Data selection
b) Data discrimination
c) Data Classification
d) Data Characterization
28. What is noise?
a) component of a network
b) context of KDD and data mining
c) aspects of a data warehouse
d) None of these
29. What is the adaptive system management?
a) machine language techniques
b) machine learning techniques
c) machine procedures techniques
d) none of these
30. An essential process used for applying intelligent methods to extract the data patterns is
named as ...
a) data mining
b) data analysis
c) data implementation
d) data computation
31. Classification and regression are the properties of...
a) data analysis
b) data manipulation’
c) data mining
d) none of these
32. A class of learning algorithm that tries to find an optimum classification of a set of
examples using the probabilistic theory is named as ...
a) Bayesian classifiers
b) Dijkstra classifiers
c) doppler classifiers
d) all of these
33. Group of similar objects that differ significantly from other objects is named as ...
a) classification
b) cluster
c) community
d) none of these
34. Combining different type of methods or information is ....
a) analysis
b) computation
c) stack
d) hybrid
35. What is the name of database having a set of databases from different vendors, possibly
using different database paradigms?
a) homogeneous database
b) heterogeneous database
c) hybrid database
d) none of these
36. What is the strategic value of data mining?
a) design sensitive
b) cost sensitive
c) technical sensitive
d) time sensitive
C.
An approach to the design of learning algorithms that is
inspired by the fact that when people encounter new situations,
they often explain them by reference to familiar experiences,
adapting the explanations to fit the new situation.
D. None of these
43. Algorithm is
A.
It uses machine-learning techniques. Here program can learn from past
experience and adapt themselves to new situations
B.
Computational procedure that takes some value as input and produces some
value as output
C.
Science of making machines performs tasks that would require intelligence
when performed by humans
D. None of these
44. Bias is
A.
A class of learning algorithm that tries to find an optimum classification of a
set of examples using the probabilistic theory
B.
Any mechanism employed by a learning system to constrain the search space
of a hypothesis
C.
An approach to the design of learning algorithms that is inspired by the fact
that when people encounter new situations, they often explain them by
reference to familiar experiences, adapting the explanations to fit the new
situation.
D. None of these
45. Case-based learning is
A.
A class of learning algorithm that tries to find an optimum classification of a set of examples
using the probabilistic theory.
B. Any mechanism employed by a learning system to constrain the search space of a hypothesis
C.
An approach to the design of learning algorithms that is inspired by the fact that when people
encounter new situations, they often explain them by reference to familiar experiences,
adapting the explanations to fit the new situation.
D. None of these
46. Classification is
A. A subdivision of a set of examples into a number of classes
B. A measure of the accuracy, of the classification of a concept that is given by a certain theory
C. The task of assigning a classification to a set of examples
D. None of these
47. Binary attribute are
A.
This takes only two values. In general, these values will be 0 and 1 and .they can be coded as
one bit
B. The natural environment of a certain species
C. Systems that can be used without knowledge of internal operations
D. None of these
48. Classification accuracy is
A. A subdivision of a set of examples into a number of classes
B. Measure of the accuracy, of the classification of a concept that is given by a certain theory
C. The task of assigning a classification to a set of examples
D. None of these
49. Cluster is
A. Group of similar objects that differ significantly from other objects
B.
Operations on a database to transform or simplify data in order to prepare it for a machine-
learning algorithm
C. Symbolic representation of facts or ideas from which information can potentially be extracted
D. None of these
50. A definition of a concept is-----if it recognizes all the instances of that concept
A. Complete
B. Consistent
C. Constant
D. None of these
D. None of these
56. Hidden knowledge referred to
A. A set of databases from different vendors, possibly using different database paradigms
B. An approach to a problem that is not guaranteed to work but performs well in most cases
C. Information that is hidden in a database and that cannot be recovered by a simple SQL query.
D. None of these
57. KDD (Knowledge Discovery in Databases) is referred to
A.
Non-trivial extraction of implicit previously unknown and potentially useful information from
data
B.
Set of columns in a database table that can be used to identify each record within this table
uniquely.
C. collection of interesting and useful patterns in a database
D. none of these
58. Learning is
A.
The process of finding the right formal representation of a certain body of knowledge in order
to represent it in a knowledge-based system
B.
It automatically maps an external signal space into a system's internal representational space.
They are useful in the performance of classification tasks.
C.
A process where an individual learns how to carry out a certain task when making a transition
from a situation in which the task cannot be carried out to a situation in which the same task
under the same circumstances can be carried out.
D. None of these
59. Inductive learning is
A.
Machine-learning involving different techniques
B. The learning algorithmic analyzes the examples on a systematic basis and makes
incremental adjustments to the theory that is learned
C.
Learning by generalizing from examples
D.
None of these
60. Naive prediction is
A. A class of learning algorithms that try to derive a Prolog program from examples
B. A table with n independent attributes can be seen as an n- dimensional space.
C.
A prediction made using an extremely simple method, such as always predicting the same
output.
D. None of these
61. Learning algorithm referrers to
A. An algorithm that can learn
B.
A sub-discipline of computer science that deals with the design and implementation of
learning algorithms
C.
A machine-learning approach that abstracts from the actual strategy of an individual algorithm
and can therefore be applied to any other form of machine learning.
D. None of these
62. Data mining is best described as the process of
a. identifying patterns in data.
b relationships in data.
c data.
d trends in data.
63. Data used to build a data mining model.
a. validation data
b. training data
c data
d data
64. Classification problems are distinguished from estimation problems in that
a problems require the output attribute to be numeric.
b problems require the output attribute to be categorical.
c problems do not allow an output attribute.
d problems are designed to predict future outcome.
65. This clustering algorithm initially assumes that each data instance represents a single
cluster.
3, 4, 5, 10, 21, 32, 43, 44, 46, 52, 59, 67
Using equal-width partitioning and four bins, how many values are there in the first bin (the
bin with small values)?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
70. High entropy means that the partitions in classification are
A. pure
B. not pure
C. useful
D. None of the above
71. A machine learning problem involves four attributes plus a class. The attributes have 3, 2,
2, and 2 possible values each. The class has 3 possible values. How many possible different
examples are there?
A. 3
B. 6
C. 12
D. 24
E. 48
F. 72
72. Which of the following is not supervised learning?
A. PCA
B. Clustering
C. Decision Tree
D. Linear Regression
73. Which of the following statements about Naive Bayes is incorrect?
A. Attributes are equally important.
B. Attributes are statistically dependent of one another given the class value.
C. Attributes are statistically independent of one another given the class value.
D. All of the above
74. Neural networks are often used for clustering.
a. True b. False
75. A rule-based classifier is determined by a set of mutually exclusive rules.
a. True b. False
76. Generally, the test error for a classifier is higher than its training error.
a. True b. False
77. The silhouette statistic is used to measure the quality of a classifier.
a. True b. False
78. our use of association analysis will yield the same frequent itemsets
and strong association rules whether a specific item occurs once or
three times in an individual transaction.
a. True b. False
79. The k-means clustering algorithm that we studied will automatically find
the best value of k as part of its normal operation.
a. True b. False
80. A density-based clustering algorithm can generate non-globular
clusters.
a. True b. False
81. In association rule mining the generation of the frequent itemsets is the
computational intensive step
a. True b. False
Neural Networks are complex ______________ with many parameters.
a) Linear Functions
b) Nonlinear Functions
c) Discrete Functions
d ) Exponential Functions
82 - A 4-input neuron has weights 1, 2, 3 and 4. The transfer function is
linear with the constant of proportionality being equal to 2. The inputs are 4,
10, 5 and 20 respectively. The output will be:
a) 238 b) 76 c) 119 d) 123
82. ANN is composed of large number of highly interconnected processing
elements (neurons) working in unison to solve problems.
a. True b. False
83. Artificial neural network used for
A.
Pattern Recognition
B.
Classification
C.
Clustering
D.
None of these
89. What is the name of node which take binary values TRUE (T) and FALSE (F)?
A. Dual Node
B. Binary Node
C. Two-way Node
D. Ordered Node
90. The ______ is the value you calculate when you want the arithmetic average.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. All of the above
91. ............................. is a summarization of the general characteristics or features of a target
class of data.
A) Data Characterization
B) Data Classification
C) Data discrimination
D) Data selection
92. ............................. is a comparison of the general features of the target class data objects
against the general features of objects from one or multiple contrasting classes.
A. Data Characterization
B. Data Classification
C. Data discrimination
D. Data selection
93. The full of KDD is ..................
A) Knowledge Database
B) Knowledge Discovery Database
C) Knowledge Data House
D) Knowledge Data Definition
94. The out put of KDD is .............
A) Data
B) Information
C) Query
D) Useful information
95. The problem of finding hidden structure in unlabeled data is called
A. Supervised learning
B. Unsupervised learning
C. Reinforcement learning
96 a rule of the form IF X THEN Y, rule confidence is defined as the
conditional probability that
a. Y is true when X is known to be true.
b. X is true when Y is known to be true.
c. Y is false when X is known to be false.
d. X is false when Y is known to be false.
97 rule support is defined as
a. the percentage of instances that contain the antecendent conditional items
listed in the association rule.
b. the percentage of instances that contain the consequent conditions listed in
the association rule.
c. the percentage of instances that contain all items listed in the association
rule.
d. the percentage of instances in the database that contain at least one of the
antecendent conditional items listed in the association rule.
98 approach is best when we are interested in finding all possible
interactions among a set of attributes.
a. decision tree
b. association rules
c. K-Means algorithm
d. genetic learning
99 choice of a data mining tool is made at this step of the KDD process.
a. goal identification
b. creating a target dataset
c. data preprocessing
d. data mining
100. Attibutes may be eliminated from the target dataset during this step of the
KDD process.
a. creating a target dataset
b. data preprocessing
c. data transformation
d. data mining
101. This step of the KDD process model deals with noisy data.
a. Creating a target dataset
b. data preprocessing
c. data transformation
d. data mining
102. A common method used by some data mining techniques to deal with
missing data items during the learning process.
a. replace missing real-valued data items with class means
b. discard records with missing data
c. replace missing attribute values with the values found within other
similar instances
C = No 5
D = No 8
Sex = Male 6
Two Item Sets Number
of Items
A= Yes & B = No 4
A = Yes & C = Yes 5
A = Yes & D = No 5
B= No & D = No 5
108. One rule that can be generated from the tables above is:
If A = Yes Then C= Yes
The confidence for this rule is:
a. 5 / 7
b. 5 / 12
c. 7 / 12
d. 1
109. Based on the two-item set table, which of the following is not a possible two-
item set rule?
a. IF C= Yes THEN A= Yes
b. IF B= No THEN A= Yes
c. IF D= No THEN A= Yes
d. IF C= No THEN D= No
Was this document helpful?
MCQ on Data mining
Course: Data Mining
91 Documents
Students shared 91 documents in this course
University: Assiut University
Was this document helpful?

Data mining questions bank with answer
1. What is the median of the following set of scores?
18, 6, 12, 10, 14 ?
a. 10
b. 14
c. 18
d. 12
2. what percentage of scores fall Approximately within one standard deviation of the mean in a
normal distribution?
a. 34%
b. 95% -→ Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean
c. 99% -→ of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
d. 68% ---→ within one standard deviation of the mean
3. ___________ is the goal to focus on summarizing and explaining a specific set of data.
a. Inferential statistics
b. Descriptive statistics
c. None of the above
d. All of the above
4. most frequently occurring number in a set of values is called the ____.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
5. the _______ is the best measure As a general rule of central tendency because it is more precise.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
6. Focusing on describing or explaining data versus going beyond immediate data and making inferences is the
difference between _______.
a. Central tendency and common tendency
b. Mutually exclusive and mutually exhaustive properties
c. Descriptive and inferential
d. Positive skew and negative skew
7. ___________ are used when you want to visually examine the relationship between two quantitative
variables.
a. Bar graphs
b. Pie graphs
c. Line graphs
d. Scatterplots
8. _______ is often the preferred measure of central tendency if the data are severely skewed.
a. Mean
b. Median
c. Mode
d. Range
9. ................... is an essential process where intelligent methods are applied to extract data patterns.
Too long to read on your phone? Save to read later on your computer
Discover more from:
Data Mining
Assiut University
91 Documents
More from:Data Mining
More from:
Data Mining
Assiut University
91 Documents
- More from:Data MiningAssiut University91 Documents
More from:Mahmoud Mohamed